A while back I wrote two posts on my personal top ten animals for the (unchilled) aquarium (here and here). Of course, there were also organisms that were not such a success. Animals can be unsuited for the aquarium for many reasons, and of course this depends on the size of aquarium, the combination of animals and what you define by ‘unsuited’; so please keep in mind that the following is a personal account!
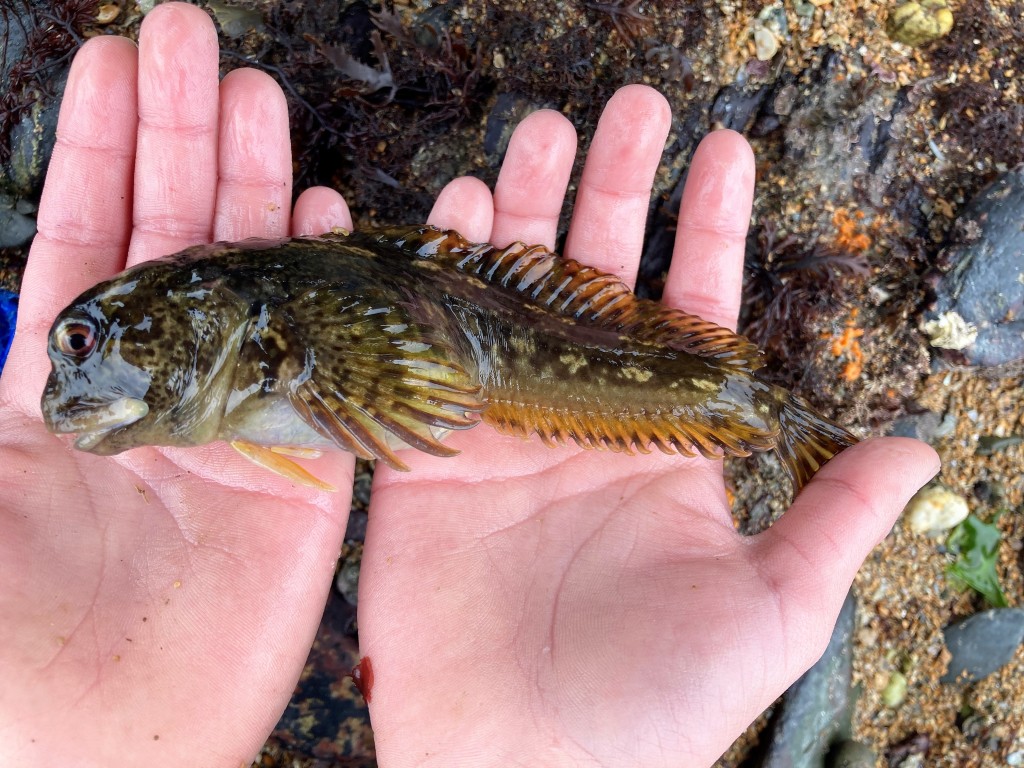
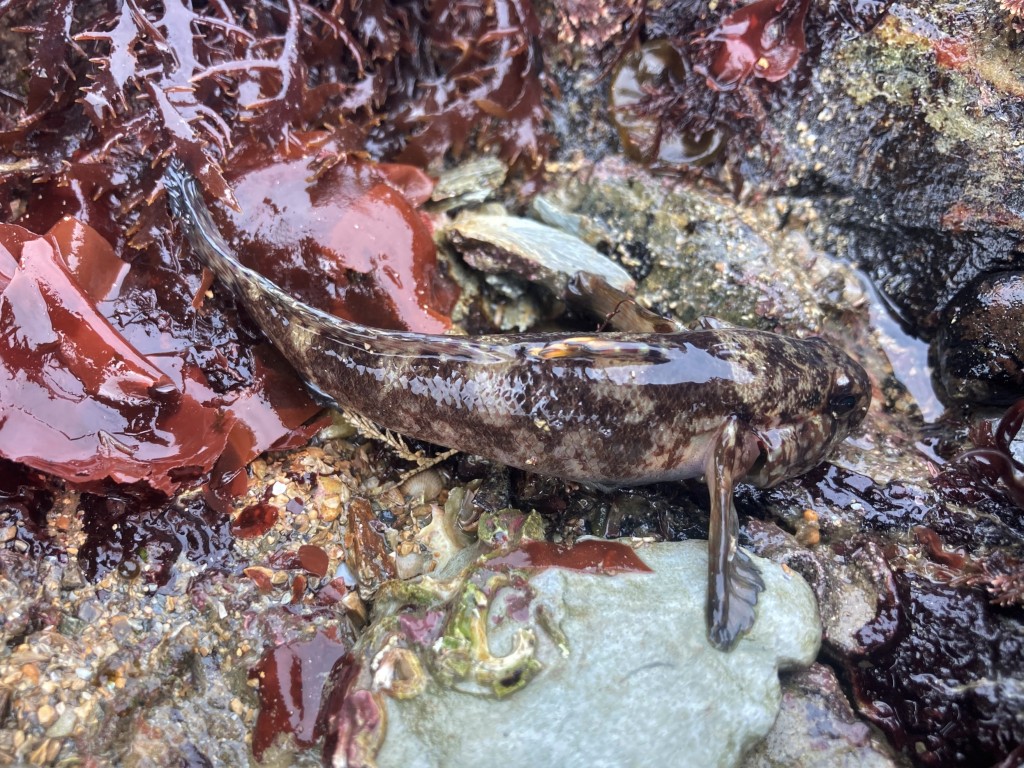
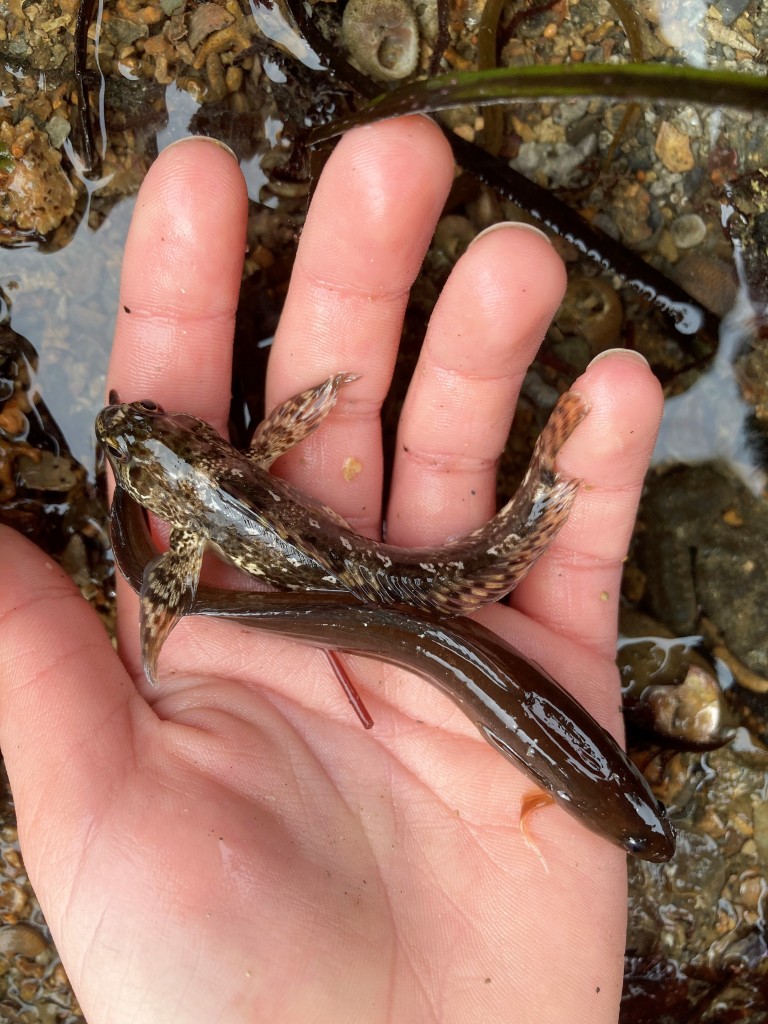
Aggressive species: Another reasons that makes animals unsuitable for a community tank is that they are bullish. (Animals becoming too big is not a real problem for the native aquarium as you can release them again and replace with smaller individuals.) Crabs often get rowdy for instance. I kept a small (5 cm carapace width) Edible crab Cancer pagurus for a little while (his name was Barry). It would bury (Barry!) itself during the day, but as soon as the lights turned off it would go about and rearrange the tank. Rocks weighing over a kilo were knocked against the glass and I found a Cushion star cut in two. It was quite an operation to remove it from the tank using a net (but during all that rummaging I interestingly saw bioluminescence in the tank which was very cool). Shannies like to feed on snails and hermit crabs and so in a relatively small aquarium at least, so sometimes you have to choose between one or the other:
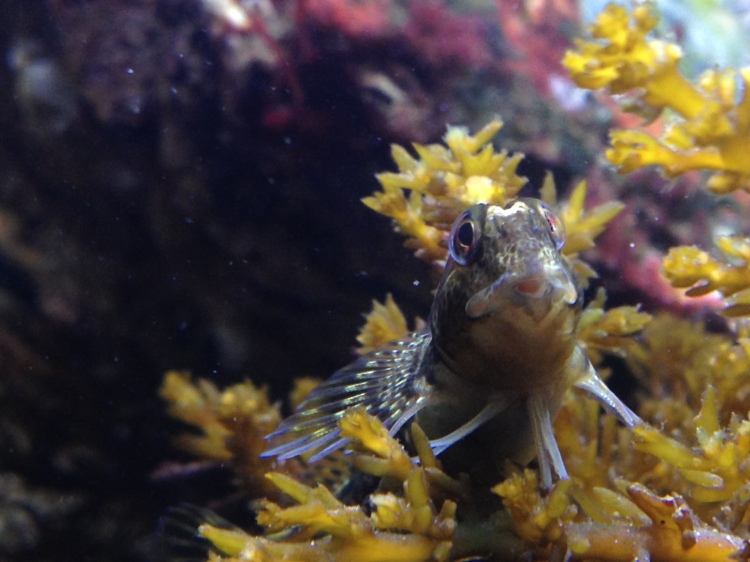

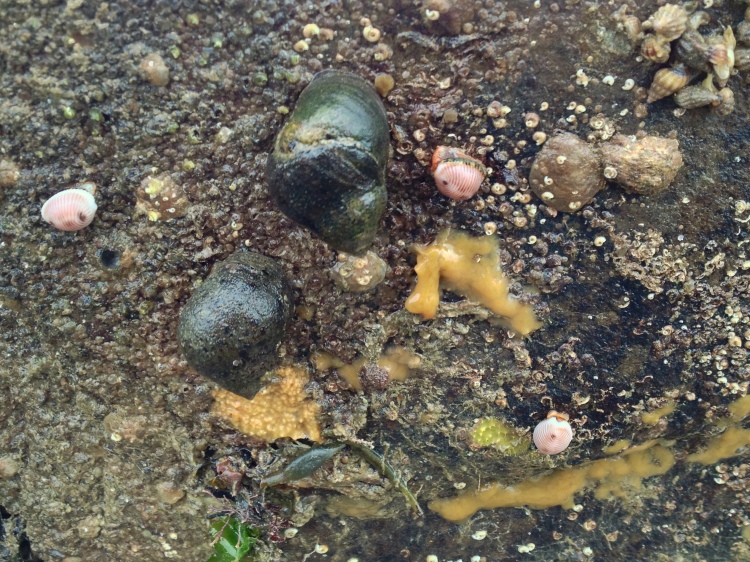
Truly littoral species: I had a couple of limpets Patella vulgata in the aquarium that just sat in the same place on the glass for months. At this time, algal growth was a problem, so I should have known if they had moved during the day or night by the tracks they would have made but they did not move a millimeter. The animals seemed a bit thinner in their shell, but seemingly they can survive for very long periods without food. Not being able to emerge from the water as they do normally seems to be a big problem for these animals.
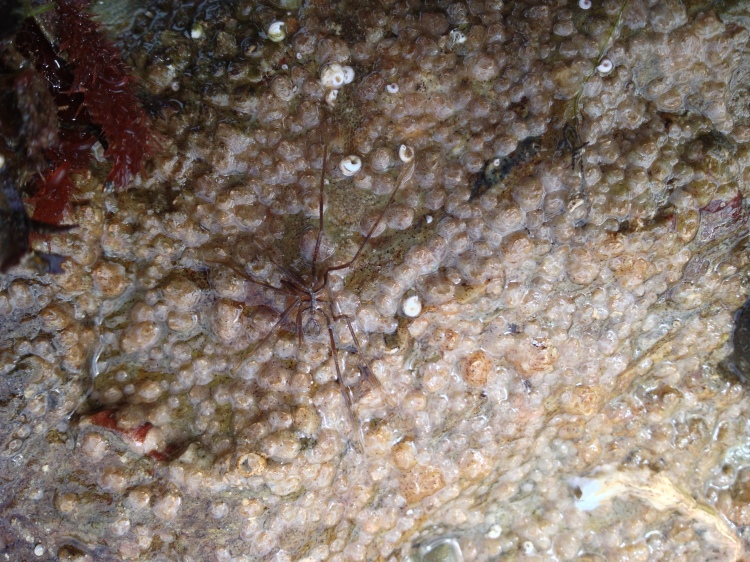
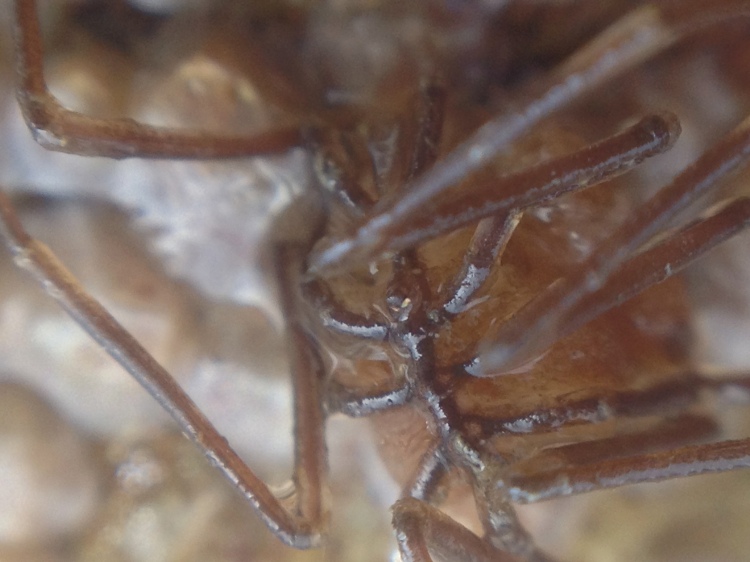
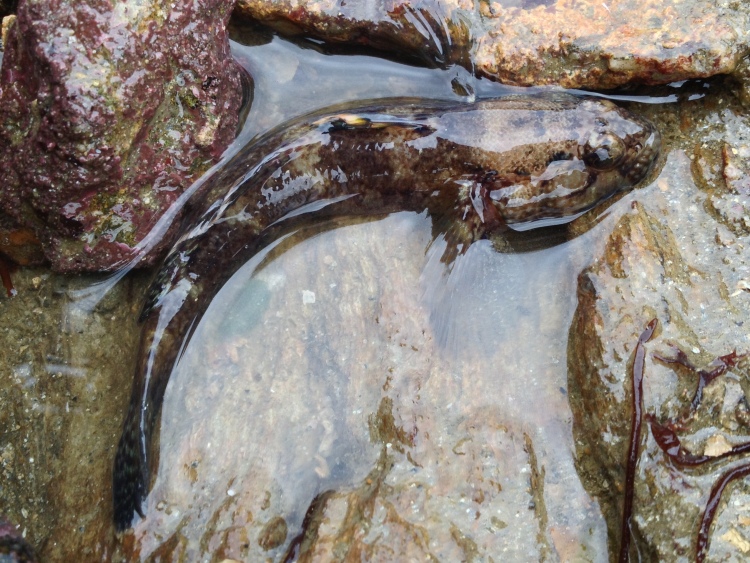
Secretive species: Other animals simply are too shy or live underneath rocks; no point really in putting them in the aquarium if you cannot see them. This happened with Broad-clawed porcelain crabs, a Shore rockling and also a Shore clingfish (although hidden, all of these animals did survive for a long time). I have seen Brittle stars in a Mediterranean aquarium but the ones found in the intertidal here tend to live under rocks and I never saw one back in the aquarium. A Sand star Astropecten irregularis quickly buried itself in the gravel:

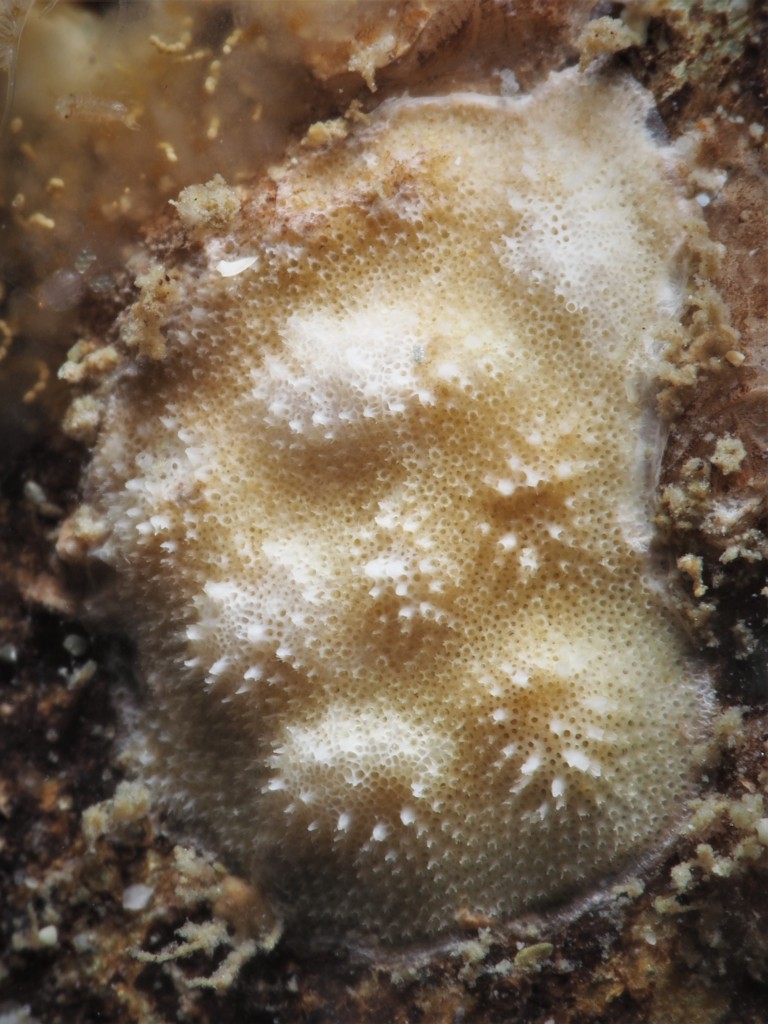
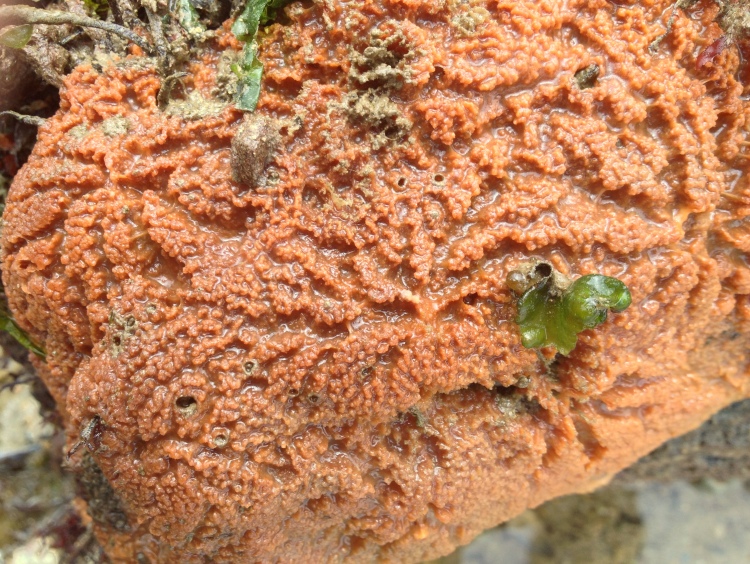
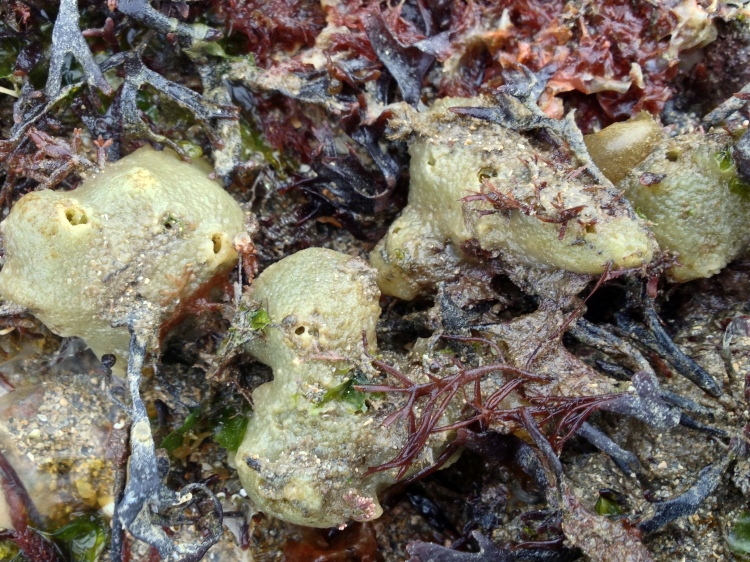
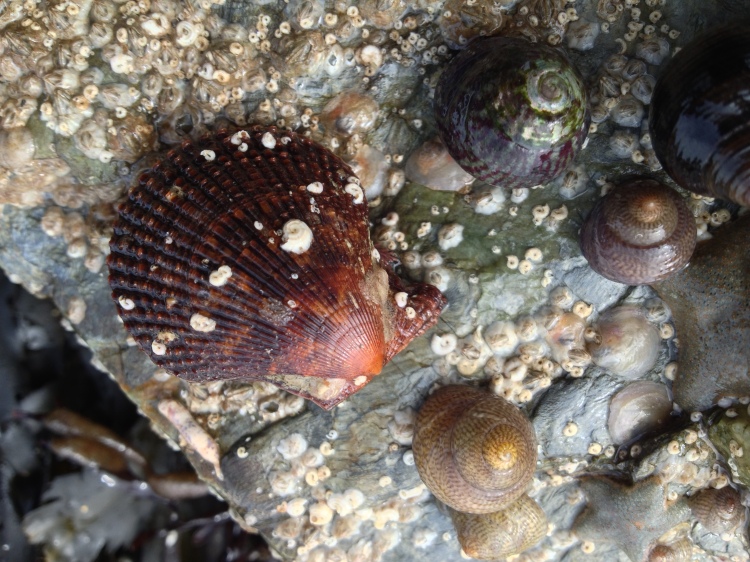
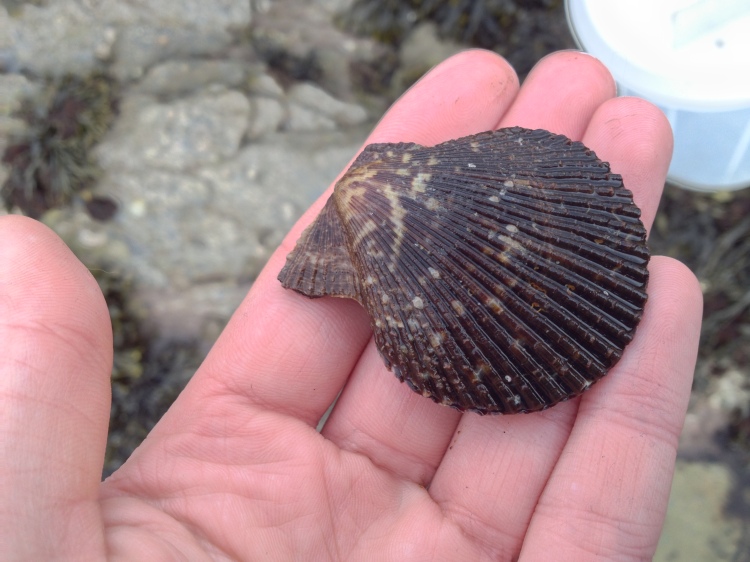
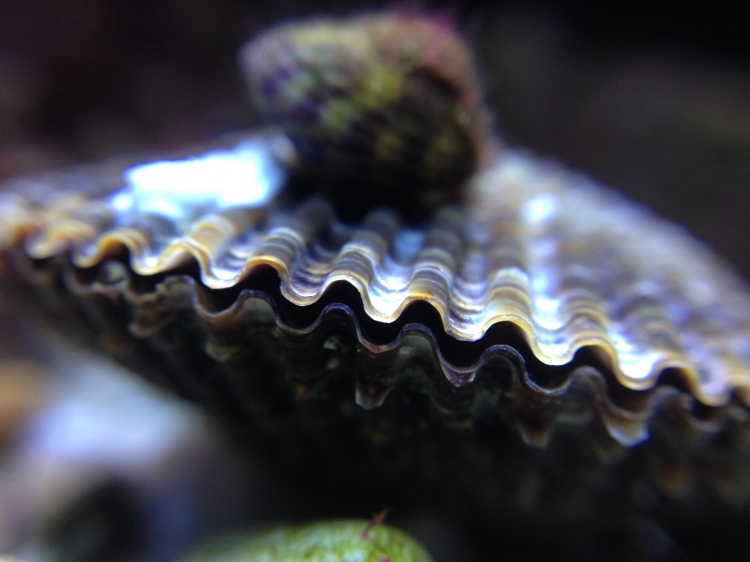
Filter feeders: I quickly realized that filter feeders, mussels or tunicates for example, were very difficult. There simply were not enough algae growing in the water to feed them (unfortunately, at times there were plenty of algae growing on the rocks and on the glass). One way to keep filter feeders is to separately cultivate algae for food. A really nice blog describing such a project can be found here. Another solution might be to feed these animals with artificial plankton, which is available commercially. This requires very good skimming to get rid of excess nutrients though. Both options I find too cumbersome at the moment. Having said all this, one filter feeder managed to survive for many months in my aquarium: the variegated scallop.
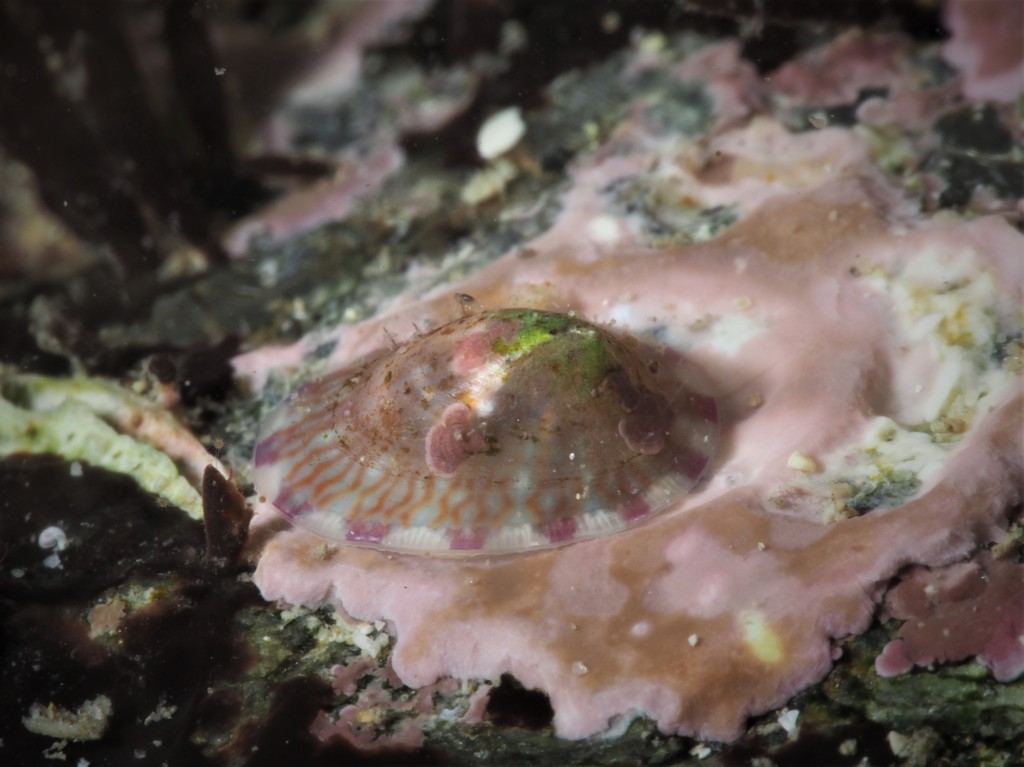
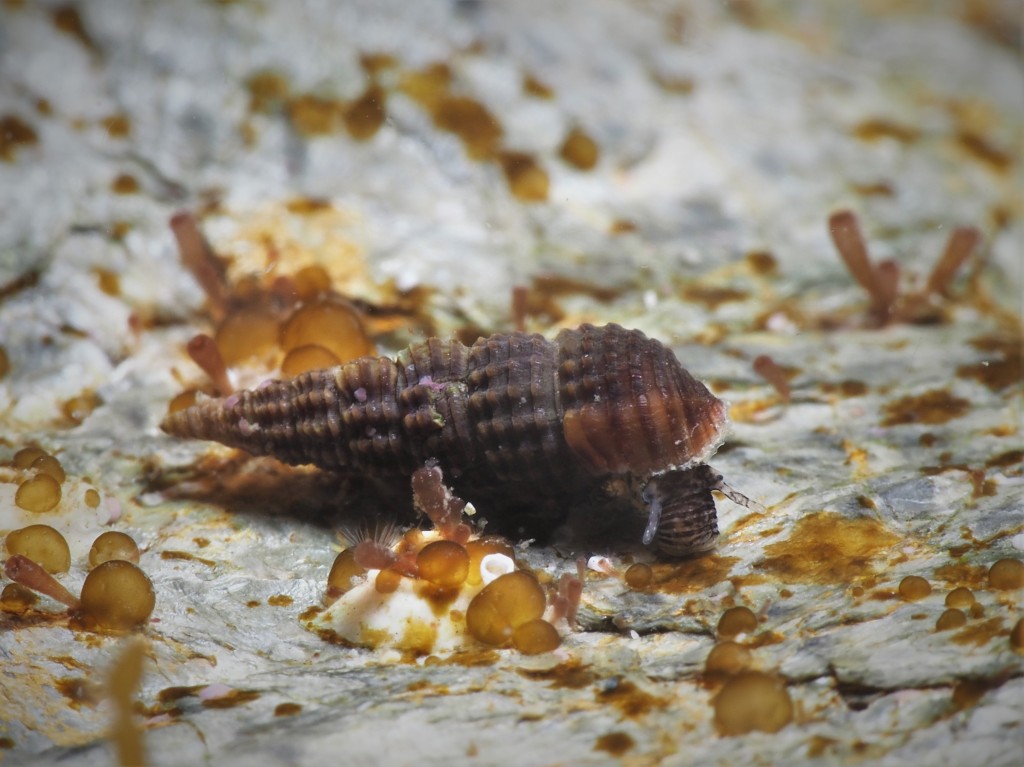
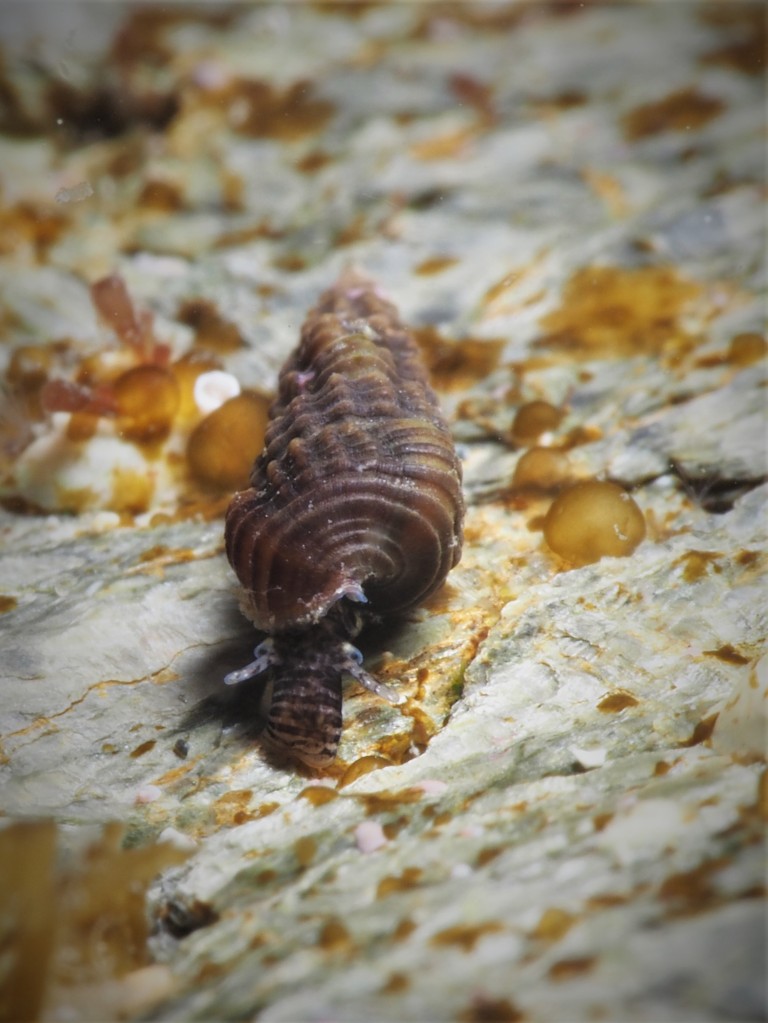
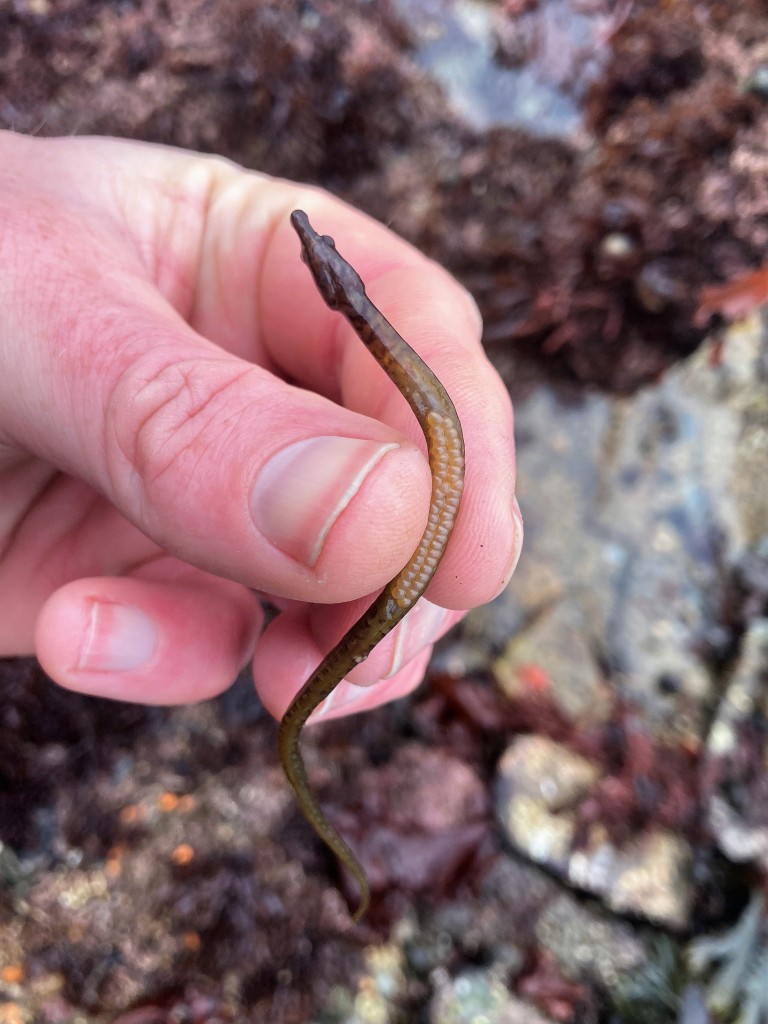
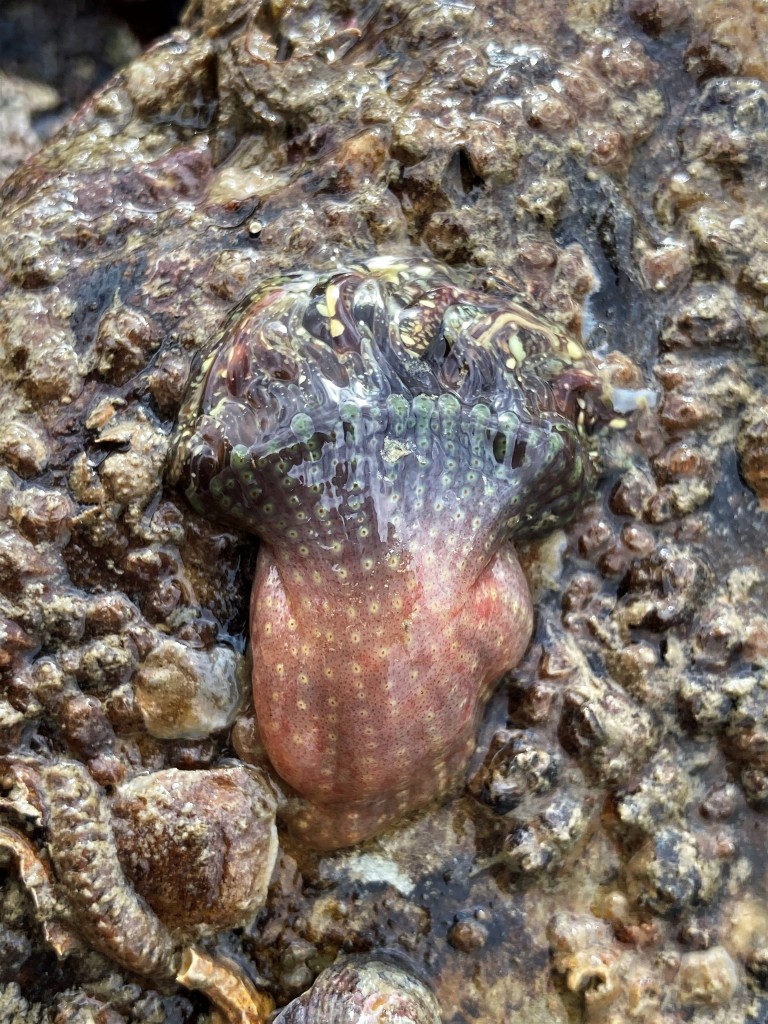
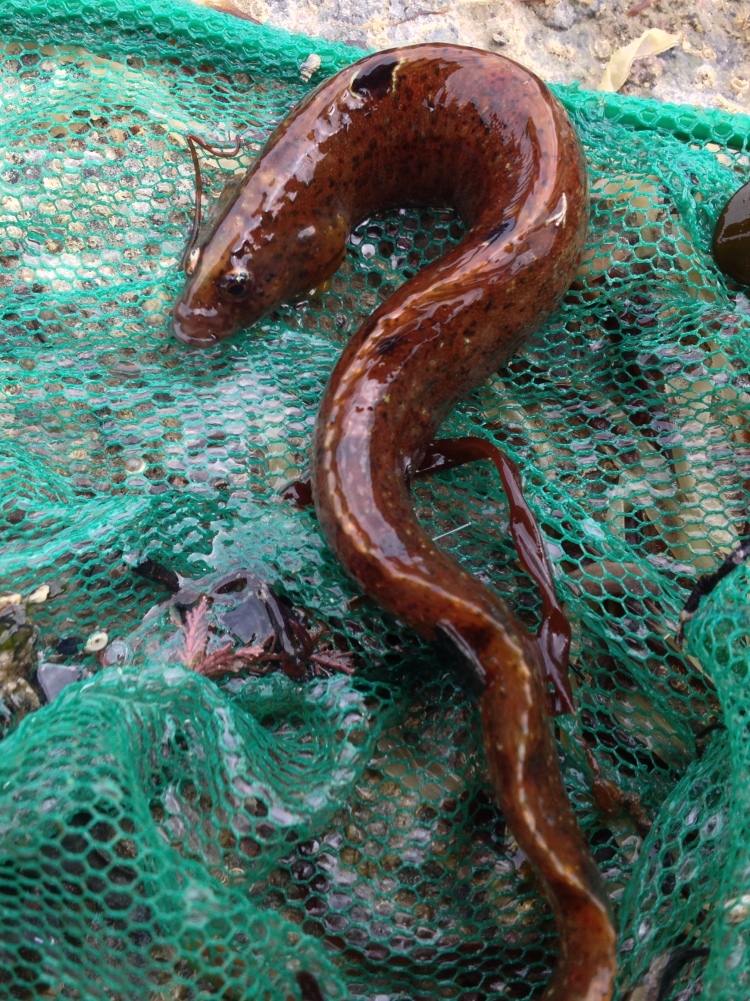
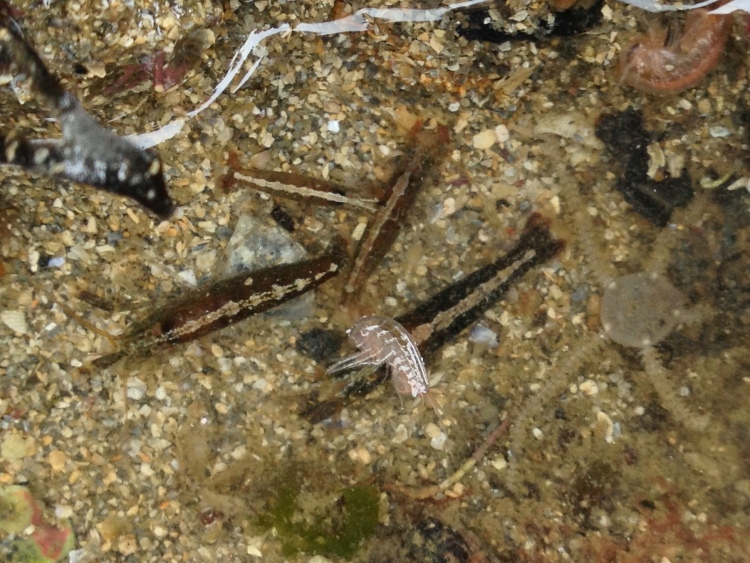
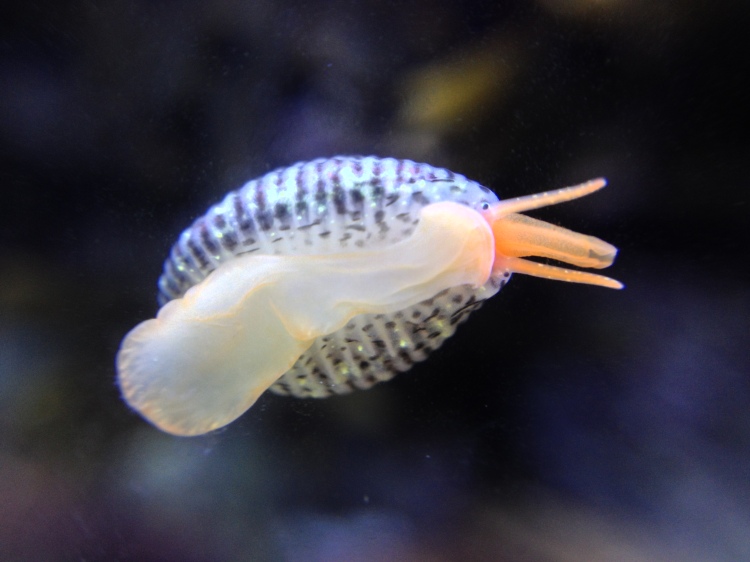
Other fussy eaters: Worm pipefish did OK in the aquarium, but that was probably because I regularly brought in new seaweeds housing fresh zooplankton. Unlike Mullet, Gobies or Blennies, I have never seen them take frozen food and therefore I will not keep them again until I can provide them regularly with live brineshrimp or similar. Snakelocks anemones always did well in the aquarium, but Beadlet and Strawberry anemones didn’t (they actually did not die but seem to shrink rather than grow over time). The former are able to grow because of their symbiosis with photosynthesizing algae and so do not rely as much on food. I must say that the latter two species are probably relatively easy to keep when you make the effort to regularly dunk a piece of dead prawn on them. The European cowrie Trivia monacha feeds on tunicates which I had trouble keeping alive and so they are unfortunately not an option yet:

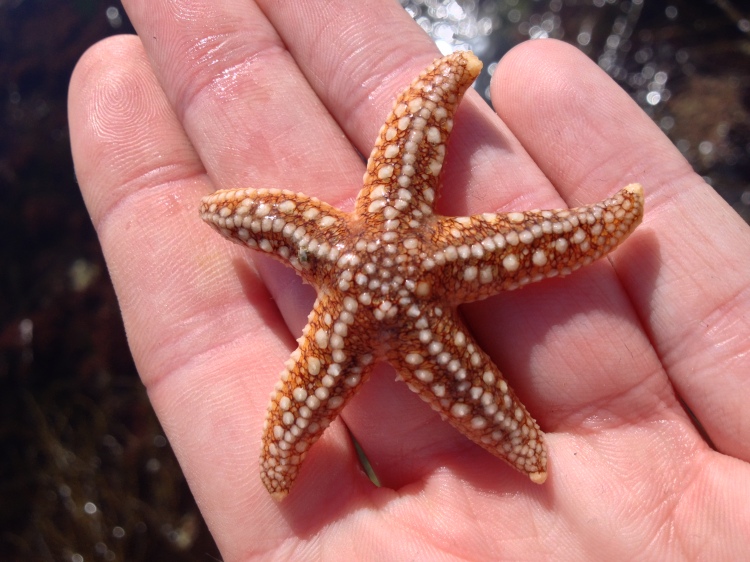
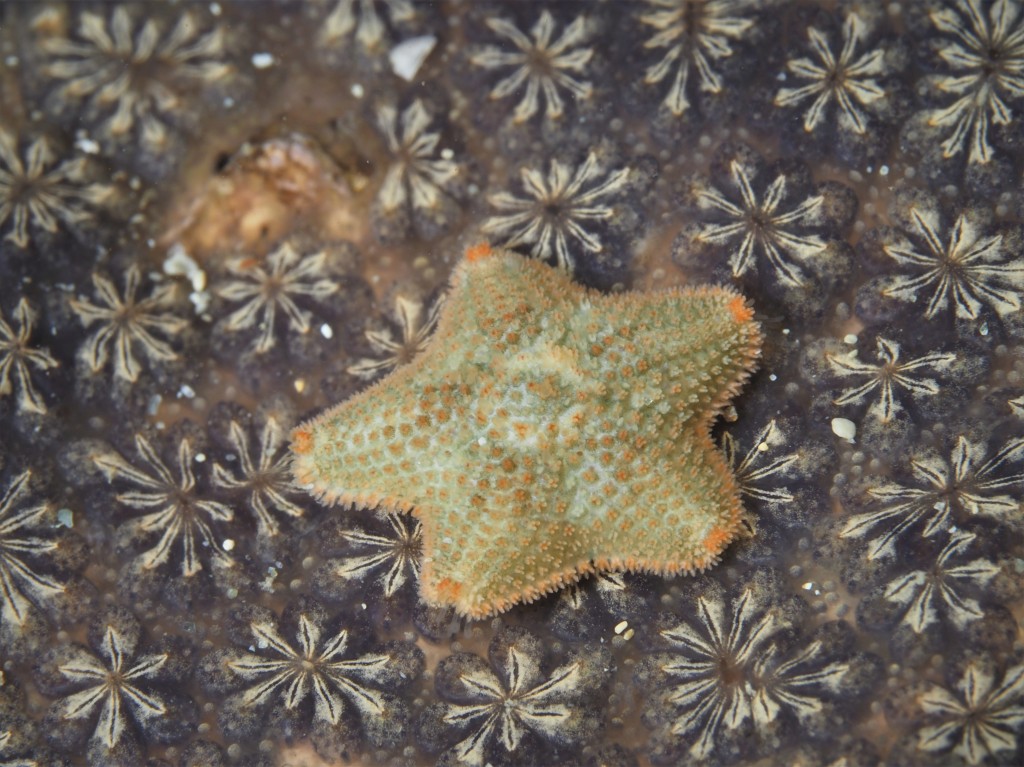
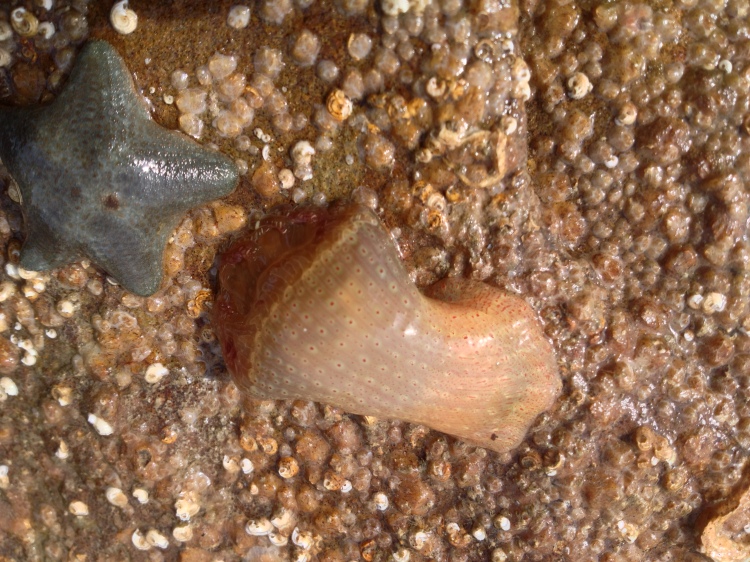
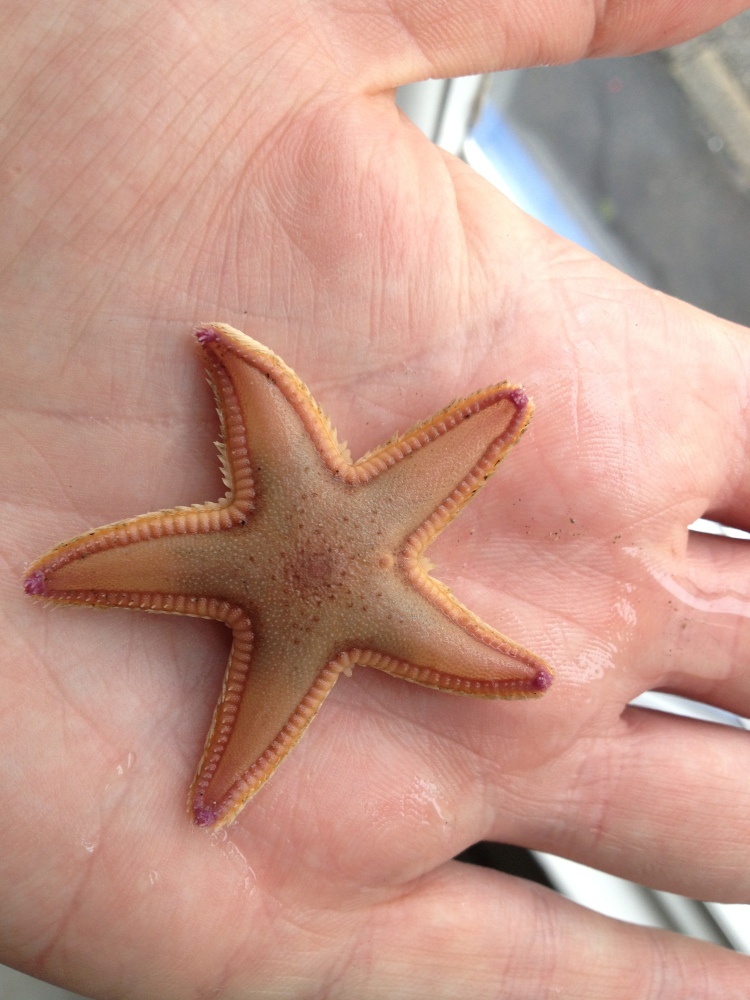
Unknown reasons: On a few occasions a species just died and I had no idea why. The only thing this taught me was to not try that species again. This happened to a Common starfish Asterias rubens: