














































Some more pics below (notice that in some another animal is lurking in the background!). Some species are easier to photograph than others, clingfish are very shy for instance. Anyway, there are some more ideas I have, for instance trying to capture multiple species in one frame and post about them in ‘The Crack pt2.’!
















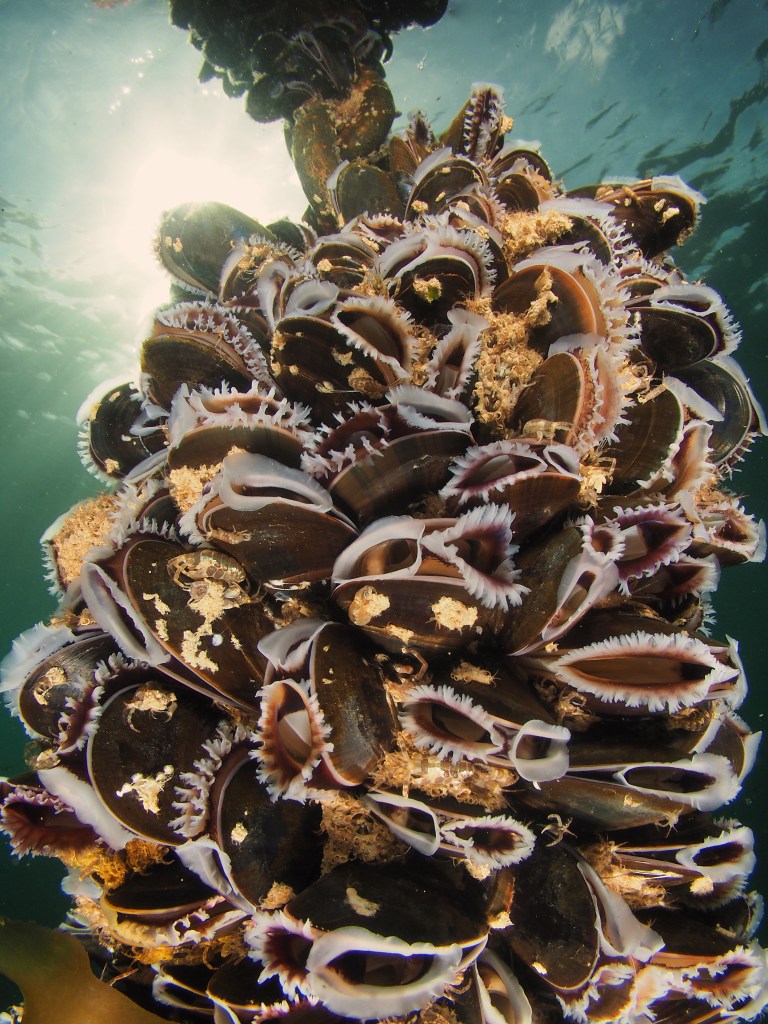
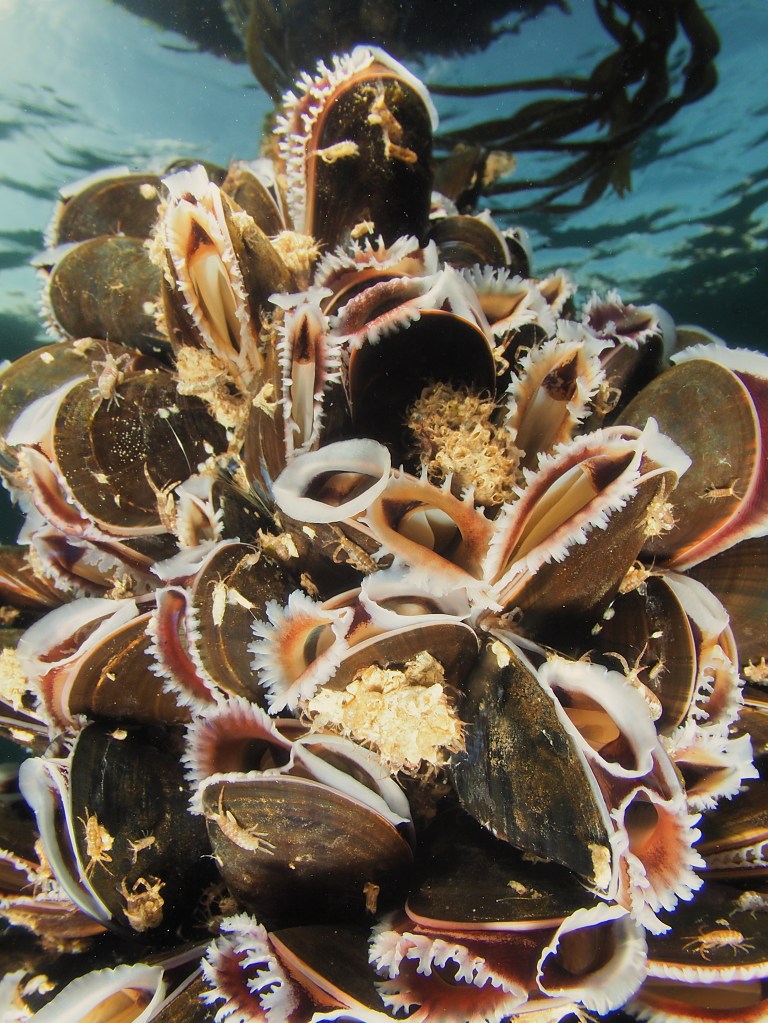
The rain has been hammering down and I am in accute underwater withdrawal… Just a bit of the ole bloggin then! These are some pictures from April, when the phytoplankton had not kicked in and the water was still quite blue. Out of curiousity I swam out to the marker buoys off Castle Beach in Falmouth to see if there was anything interesting growing on them. There was! Lots of mussels, including on the chain going down to the bottom (10ish meters deep). I took my fisheye lens and after much adjusting of strobes (holding the housing sideways for portrait mode, and also up, meaning that the lower strobe needed to be pulled back) I got the nice shot above. Mussels are not a favourite of underwaterphotographers (this is an understatement!) but they are beautiful upclose, the white mantle contrasting with the blueish black shell.
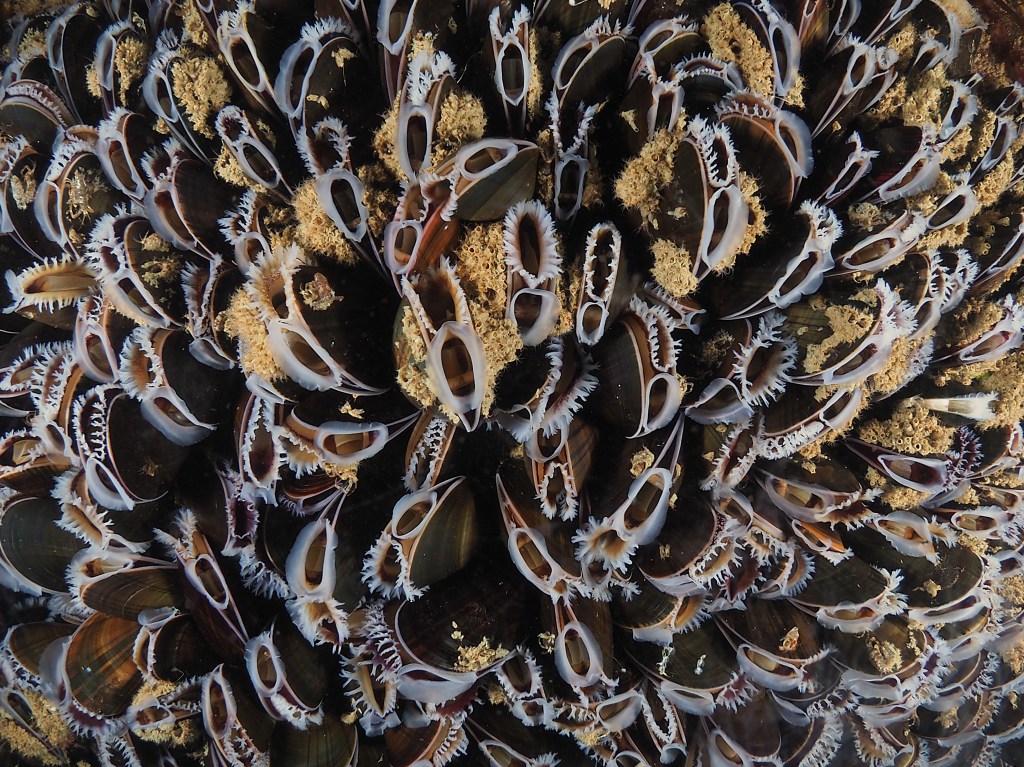

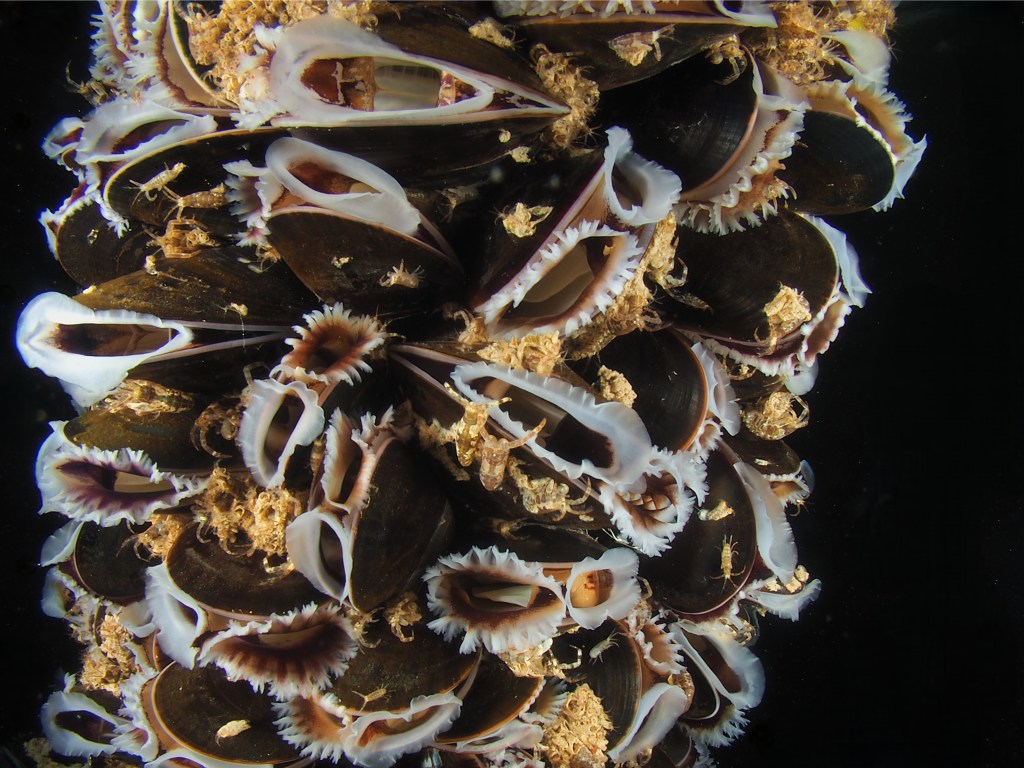
A few days later I returned with my probe lens, as i thought this would offer an original perspective. It was a tricky thing to do as this lens lets in very little light. The difference between foreground and background seems slightly off as well! These photos show that the mussels were crawling with the tubedwelling amphipod Jassa marmorata, a prominent fouling species. I planned to return to try again a few days later, but the chains had been replaced by ‘fresh’ ones, bad luck! I will go back to have a look at them as soon as the weather allows it.



P.S. there are two older posts tagged with ‘buoys‘.
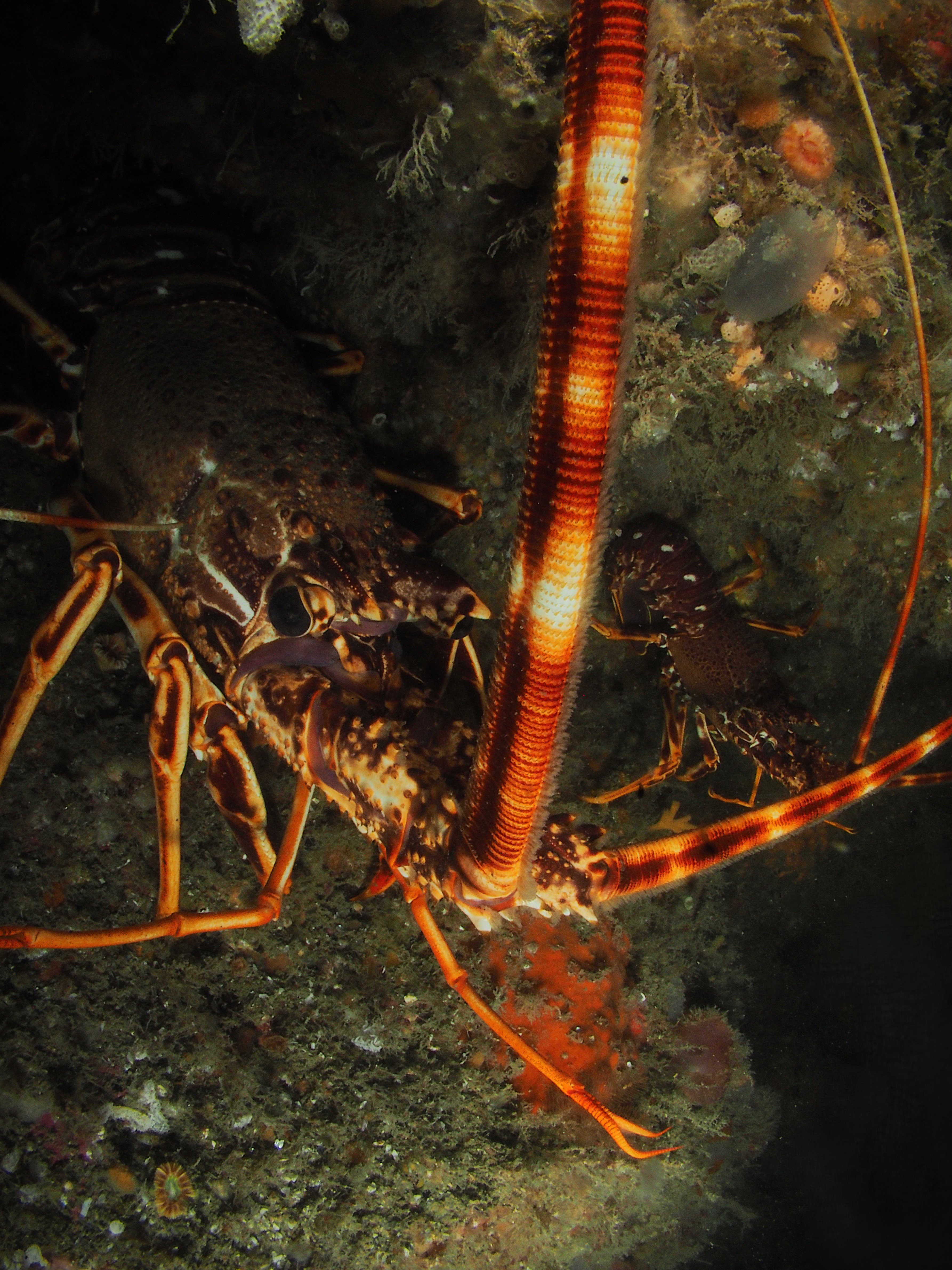
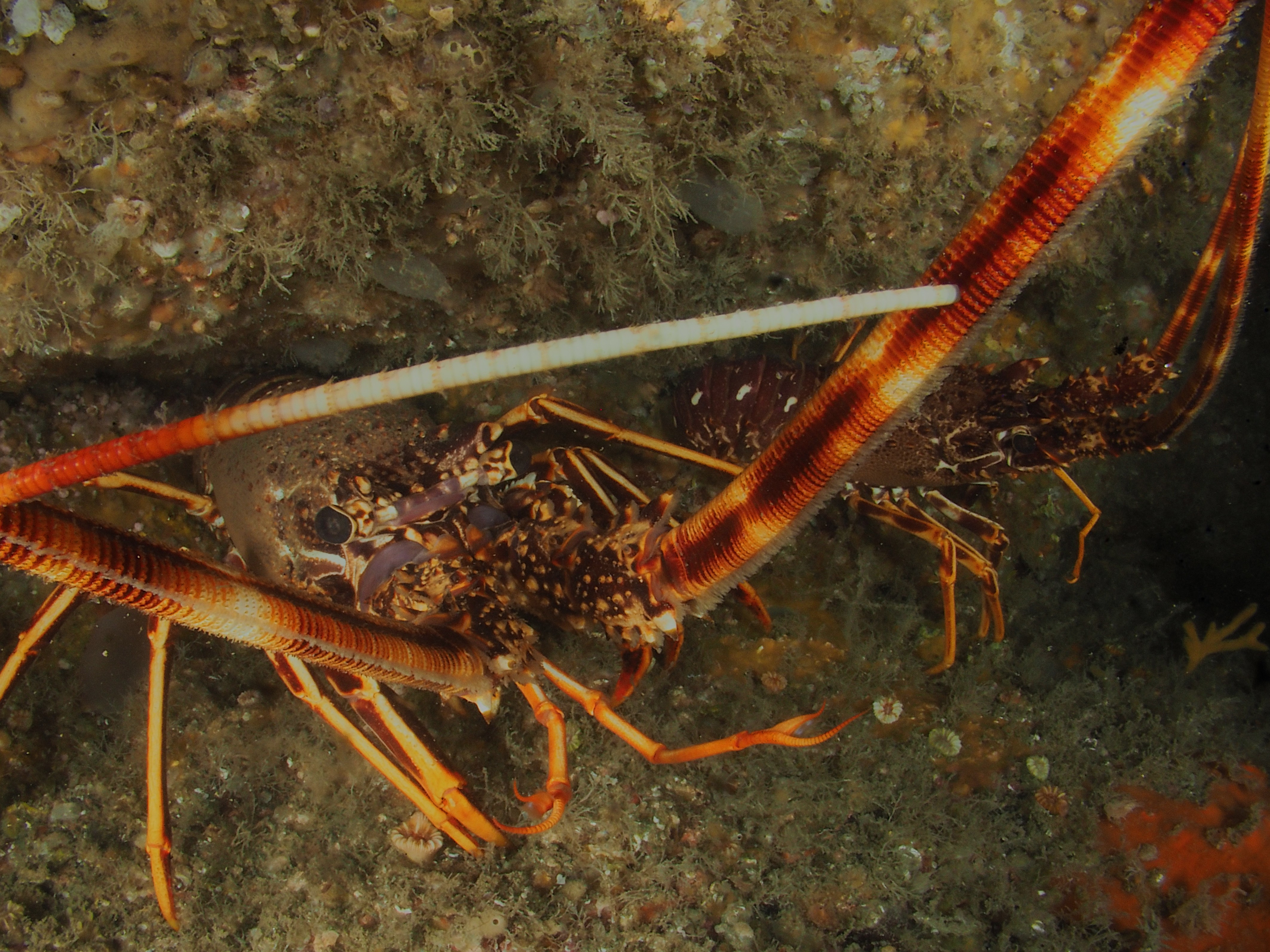
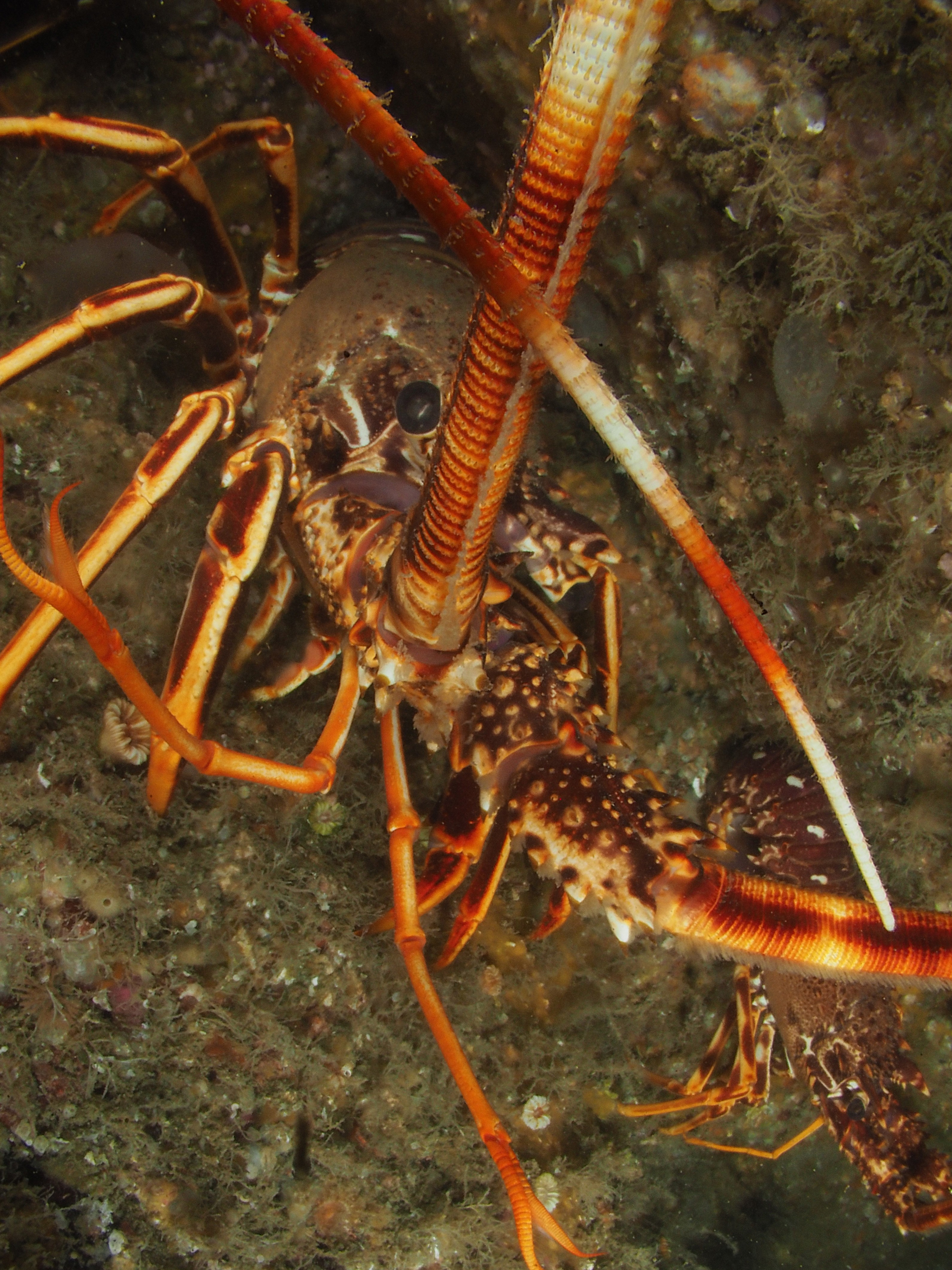
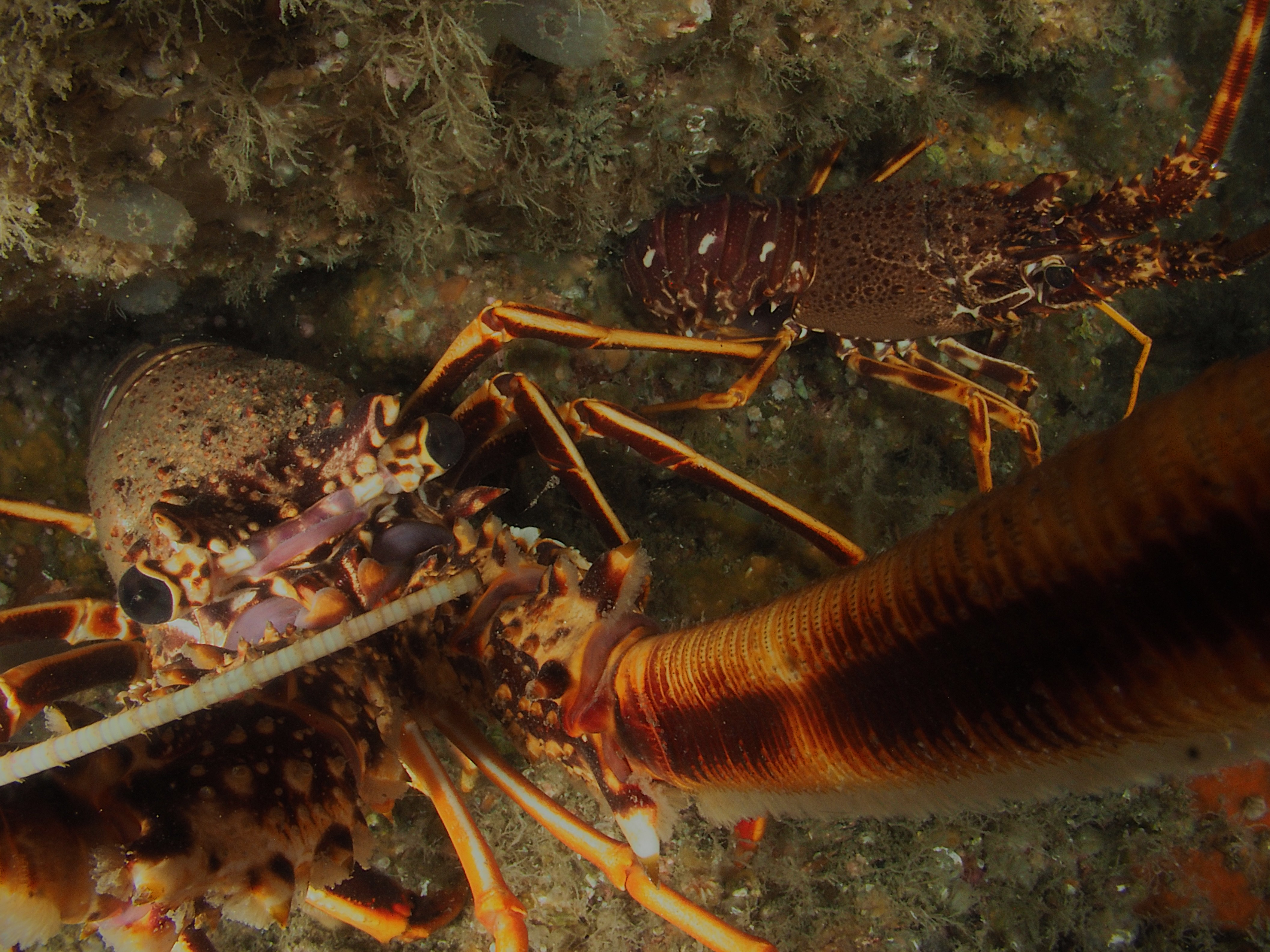
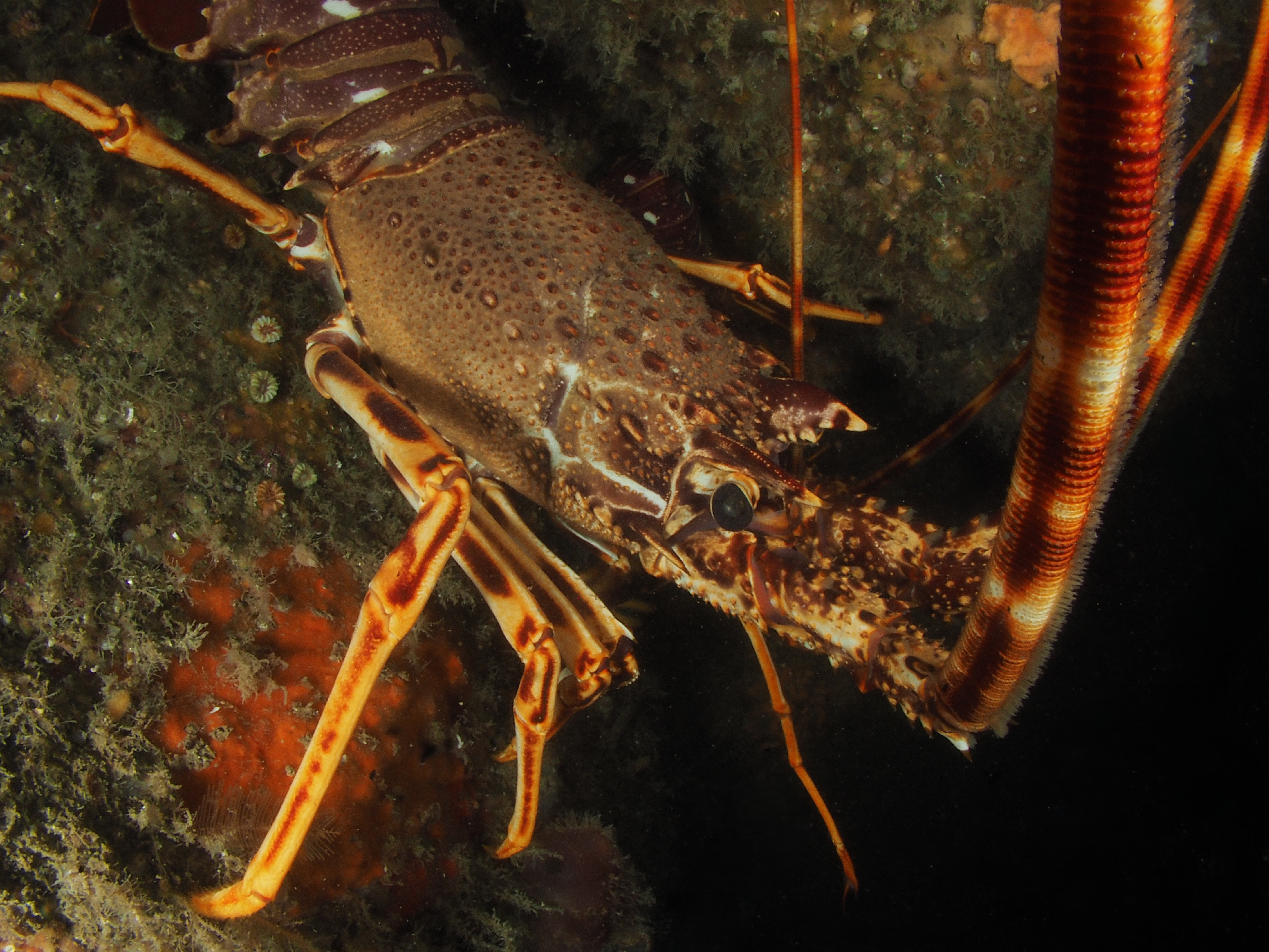






























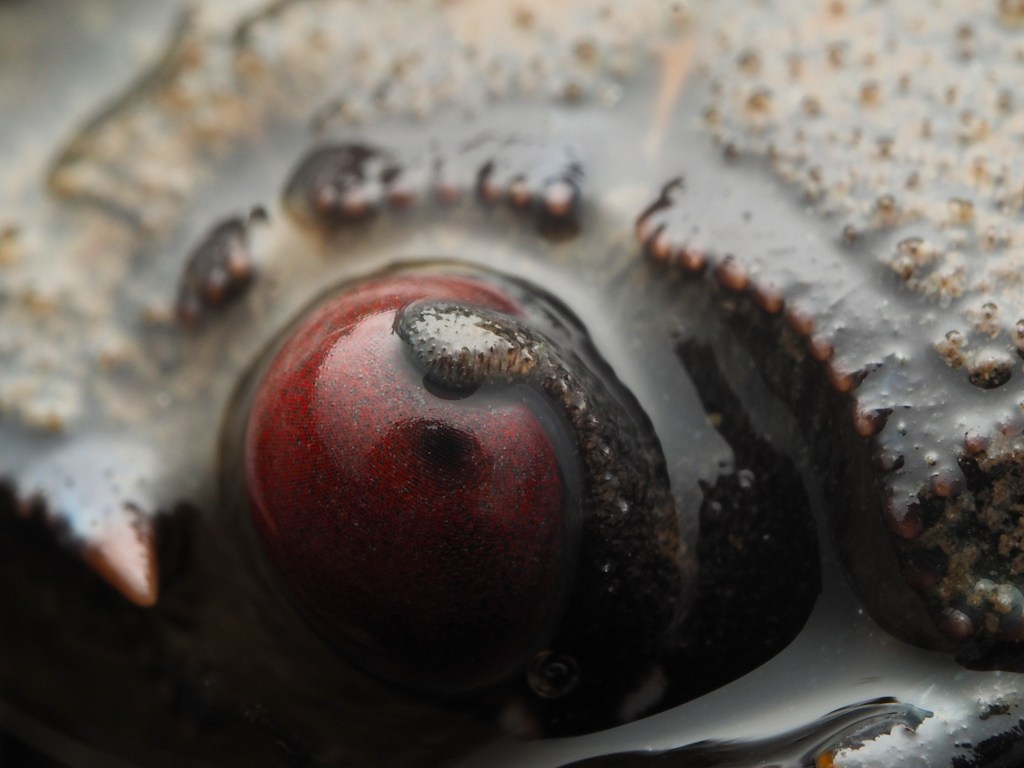
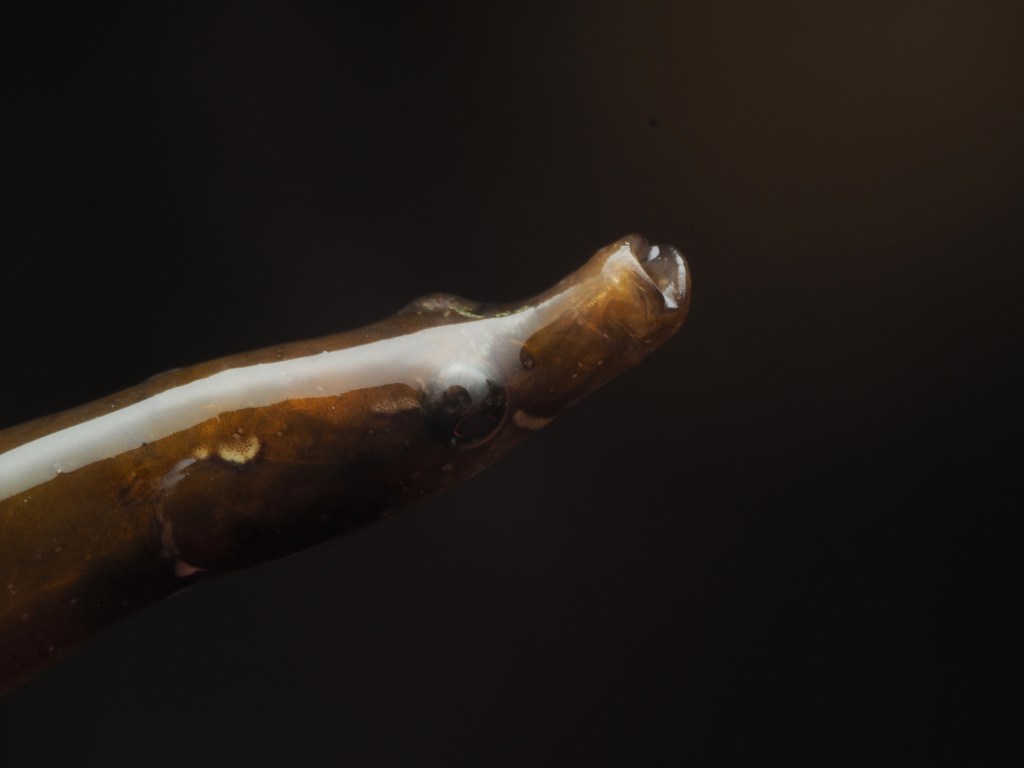
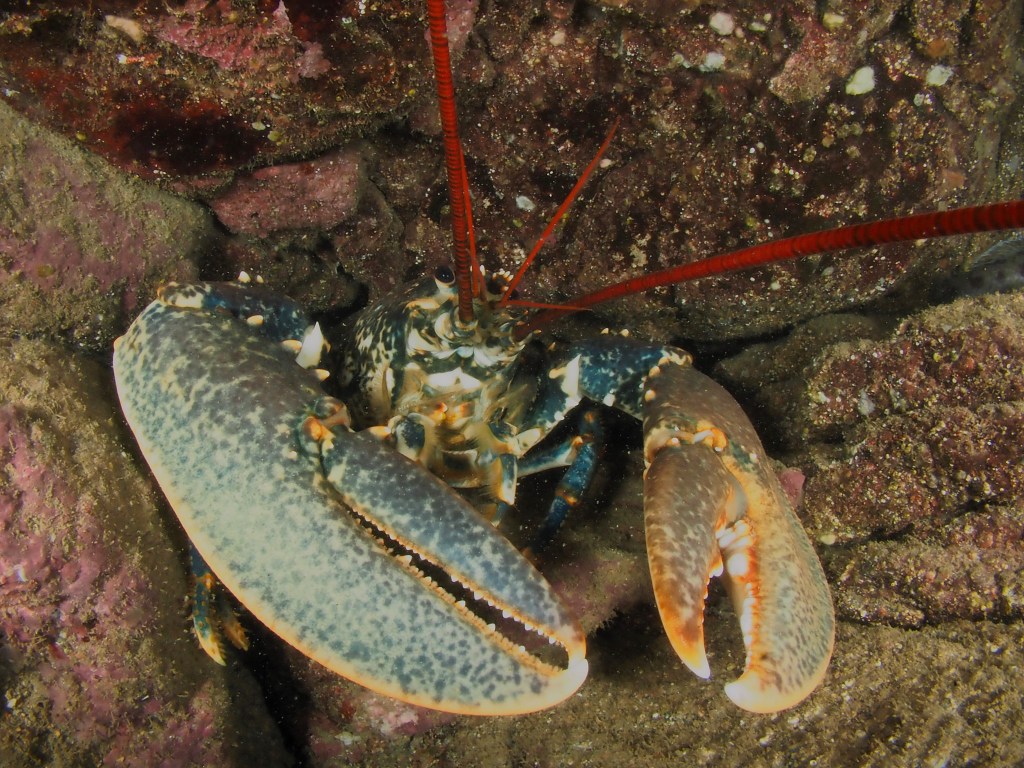
I have done a fair bit of diving at Silver Steps this year and it is high time to publish some of the photos I took there, starting with the Crustaceans that inhabit the cracks in the rocks. Most pics were taken with the macro-wide angle lens, which is not only suited because of its perspective, but also because it is long and thin and so can be poked into the crevices where these creatures lurk. Above, two Velvet Crabs Necora puber, which are abundant and feisty – I only noticed the small female in the photo afterwards! Below a European Lobster Homarus gammarus, also quite common and some of them are quite big. They usually shuffle out of their den quite menacingly only then to retreat again. Although impressive animals, it is hard to get an aesthetically pleasing shot out of them I find.

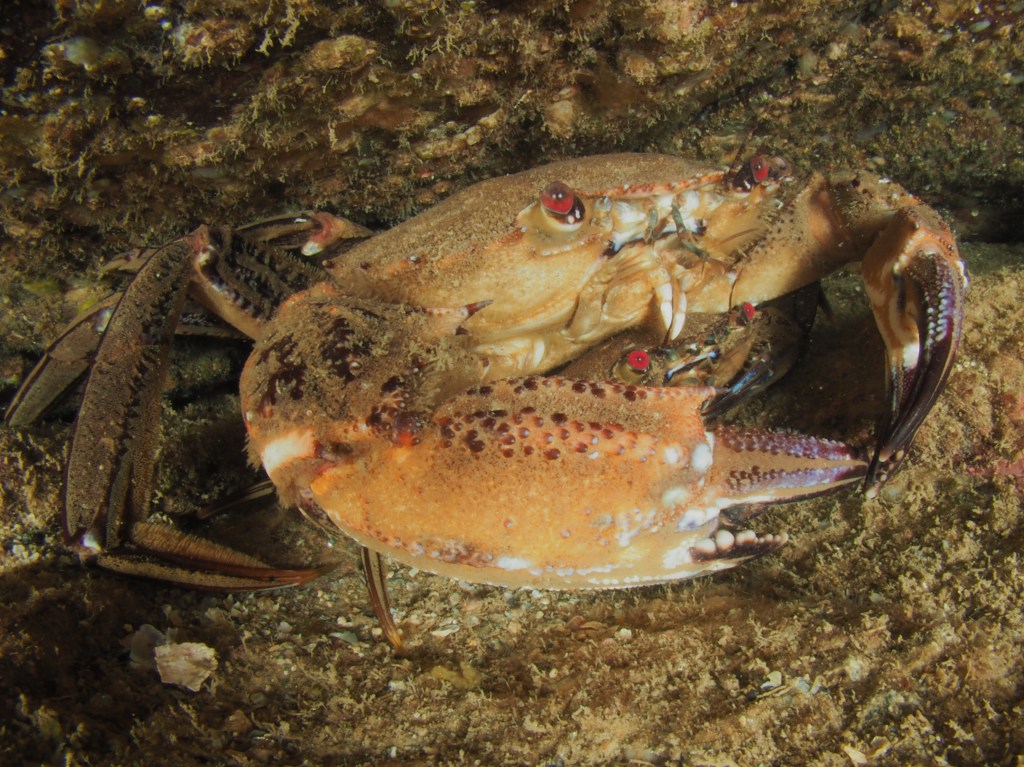
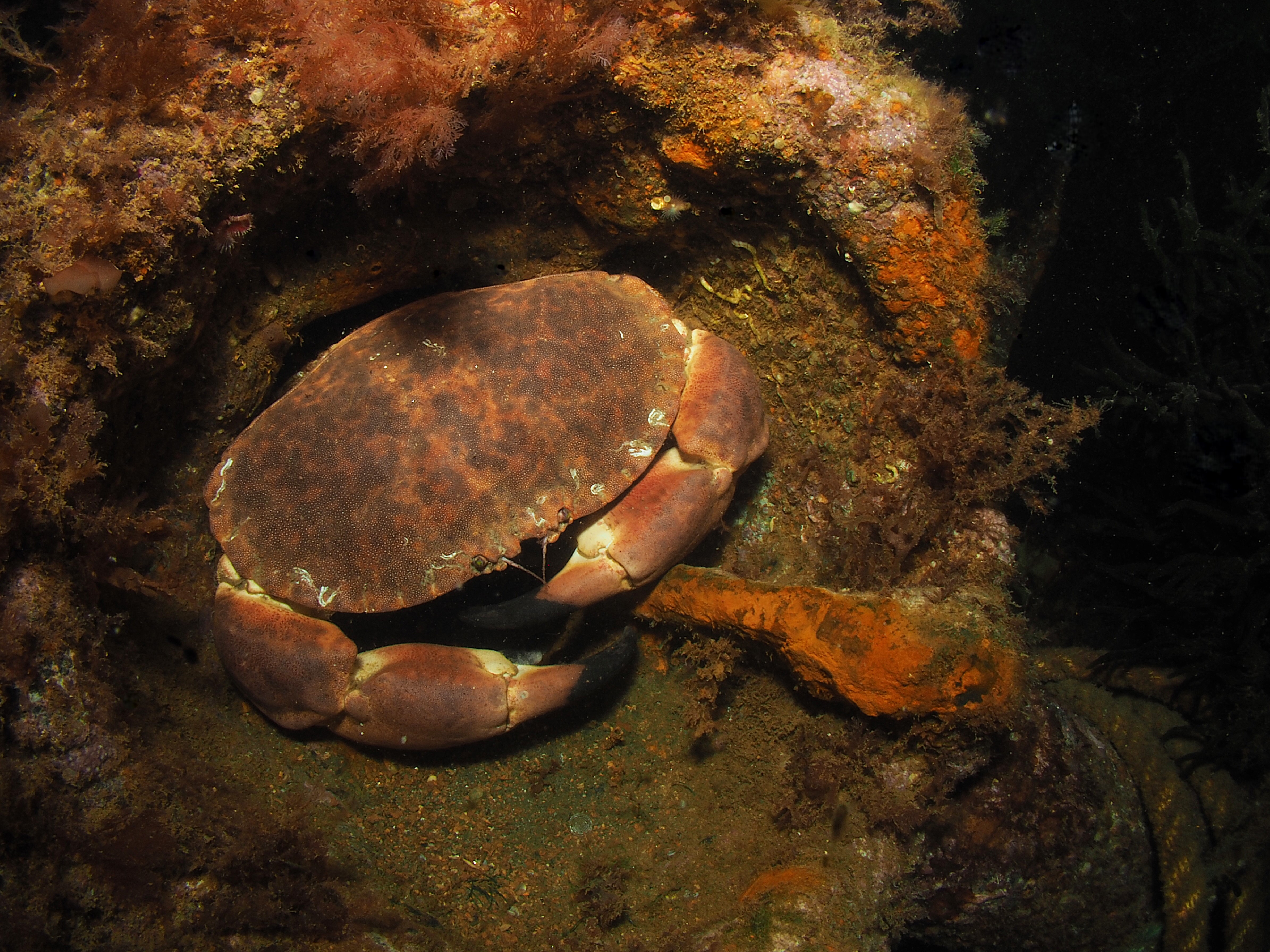
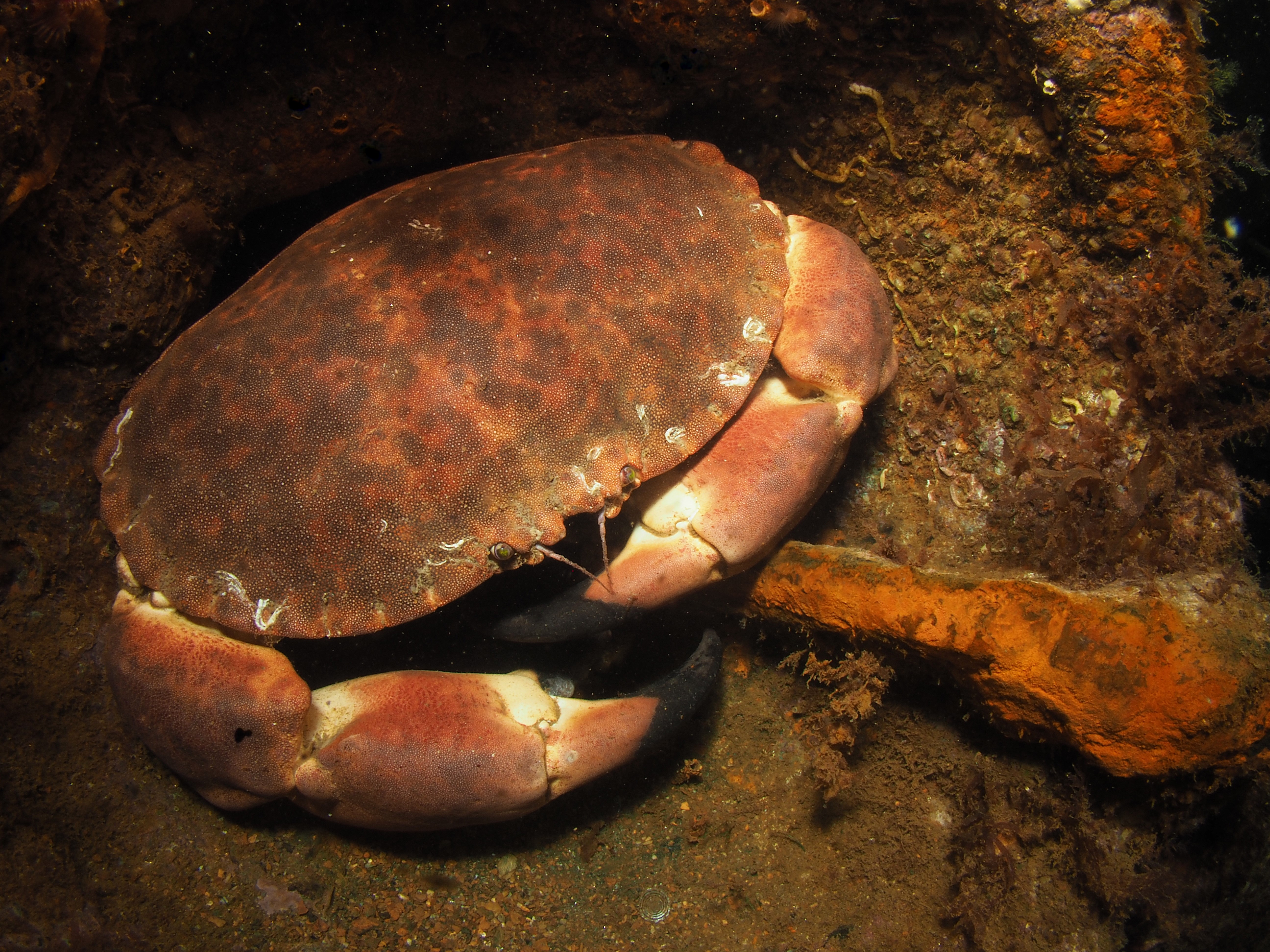
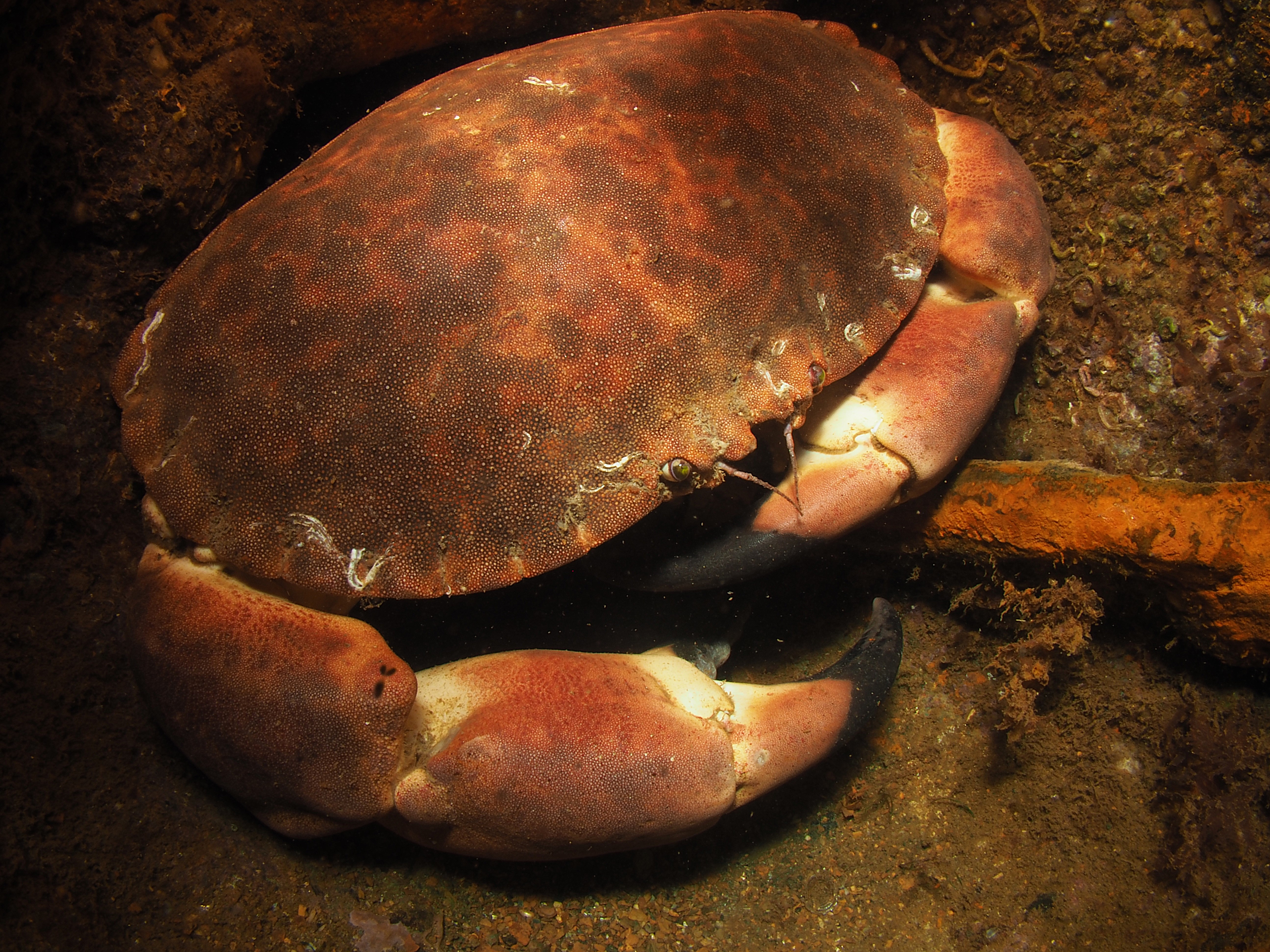
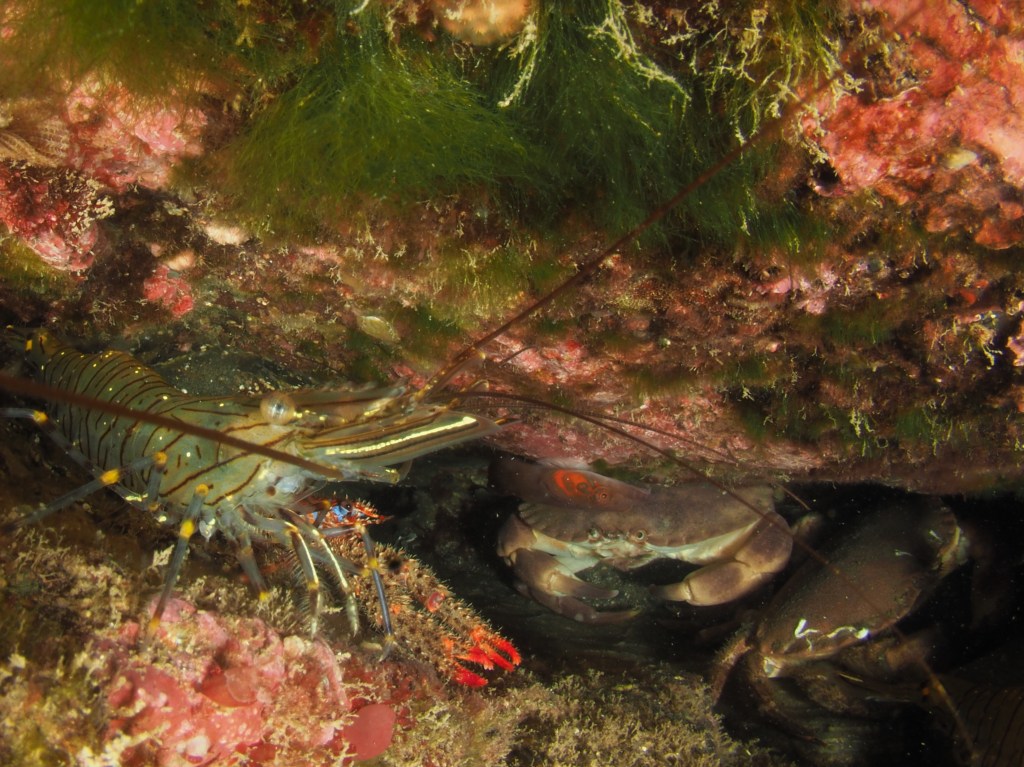
Next, the Squat Lobster Galathea strigosa, also a common, but quite shy species which is just as happy upside down as right side up. Also common are Brown (or Edible) Crabs Cancer pagurus, the individual here not in a crevice but in a piece of steel wreckage.
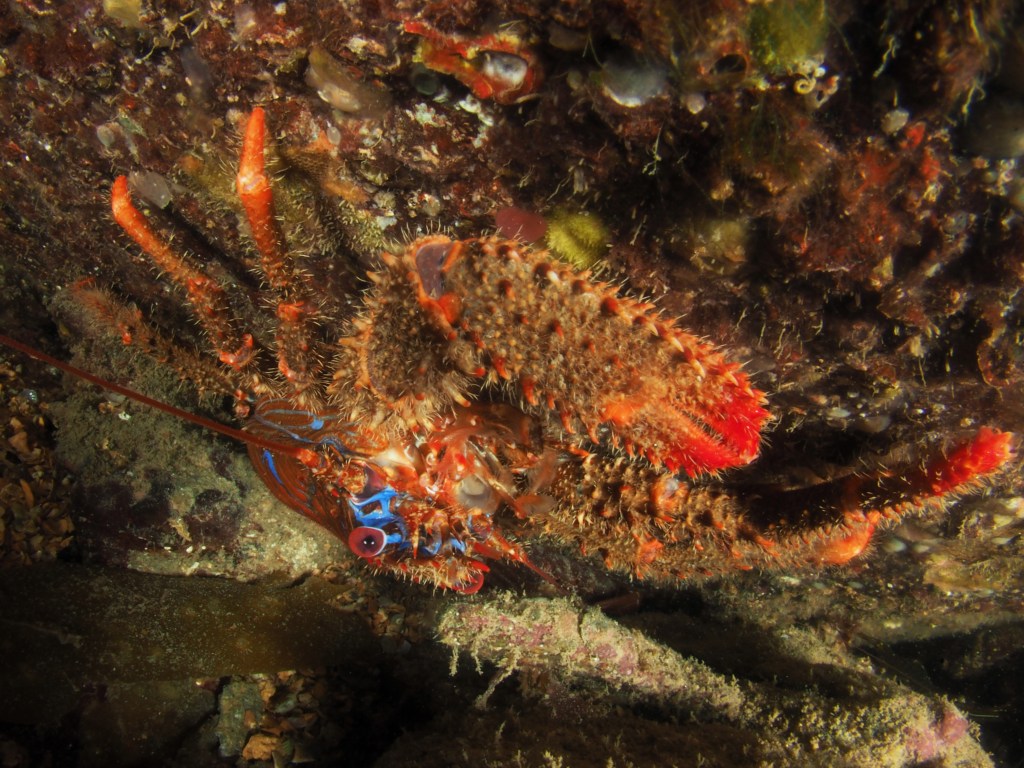




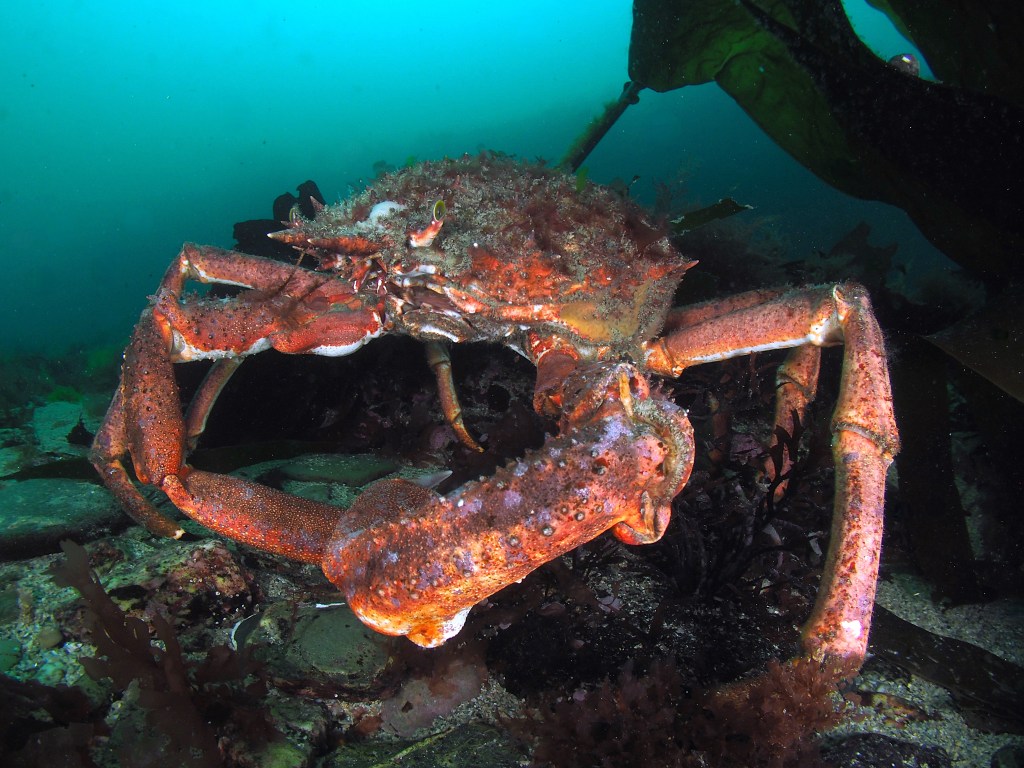
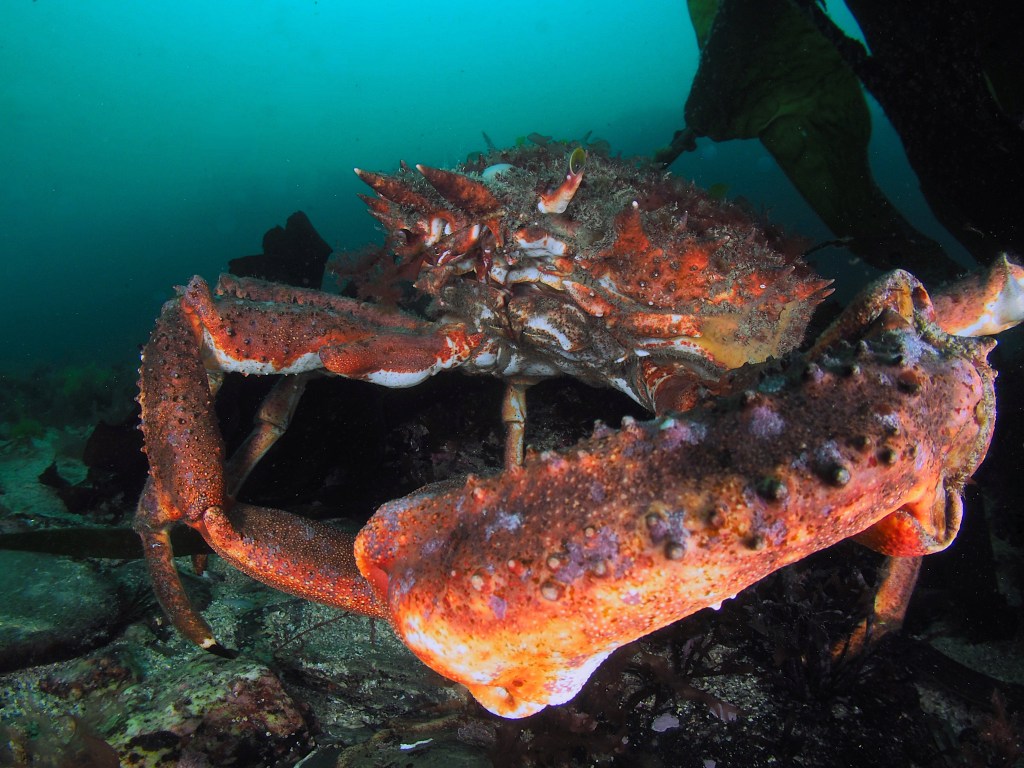
The other big, common Crustacean here occasionally perches on rock walls but usually is found roaming the seabed: the European Spider Crab (rebranded by local fishmongers as ‘Cornish King Crab’ – sounds more appetizing than something spiderlike) Maja squinado brachydactyla. Like the lobster, the behaviour of these guys is a mixture of bravado and fear. The weird lens allows me to get close, but as it lets in very little light, I am forced to use a high ISO and slow shutterspeed, making these images not the crispiest.


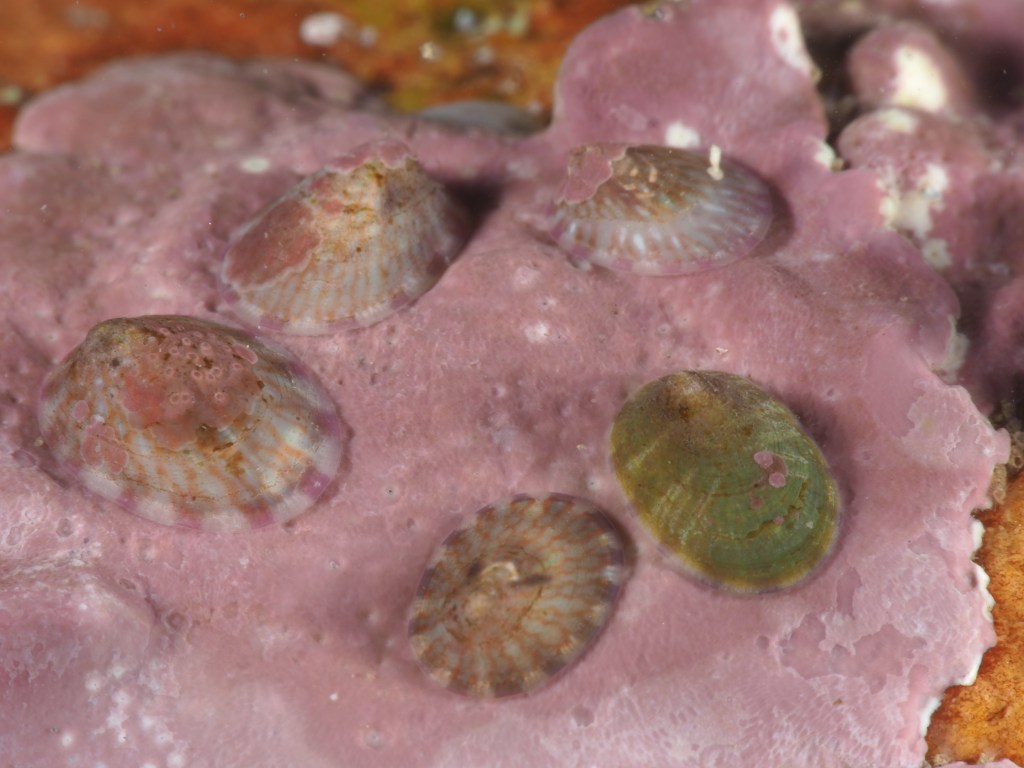
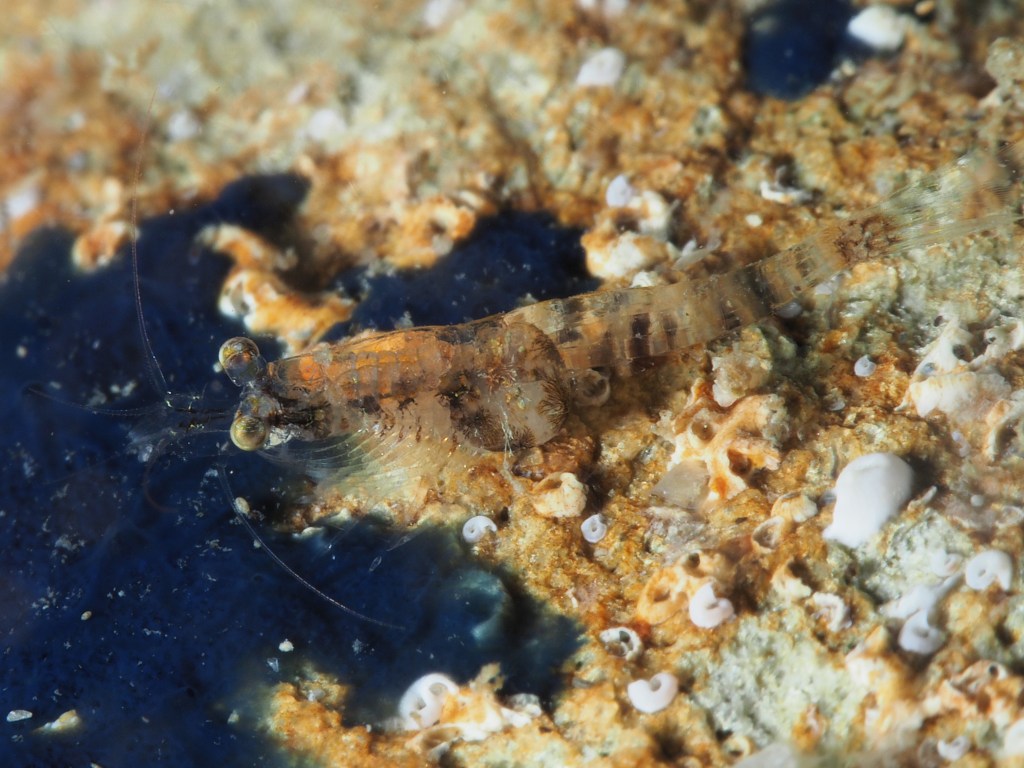
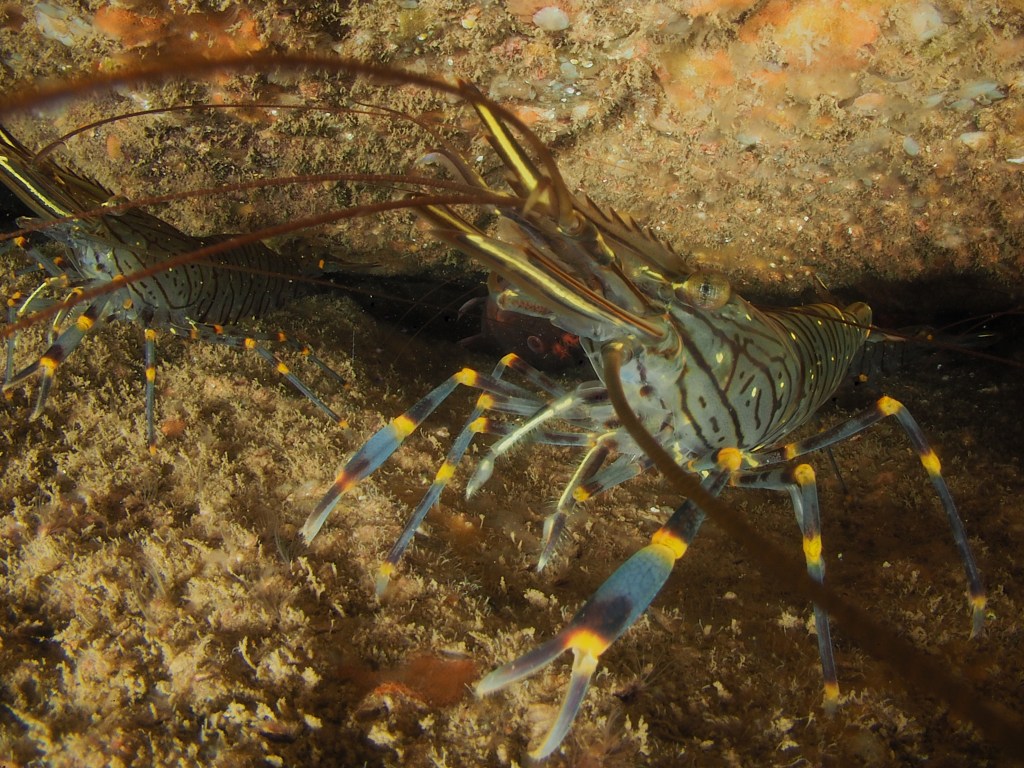
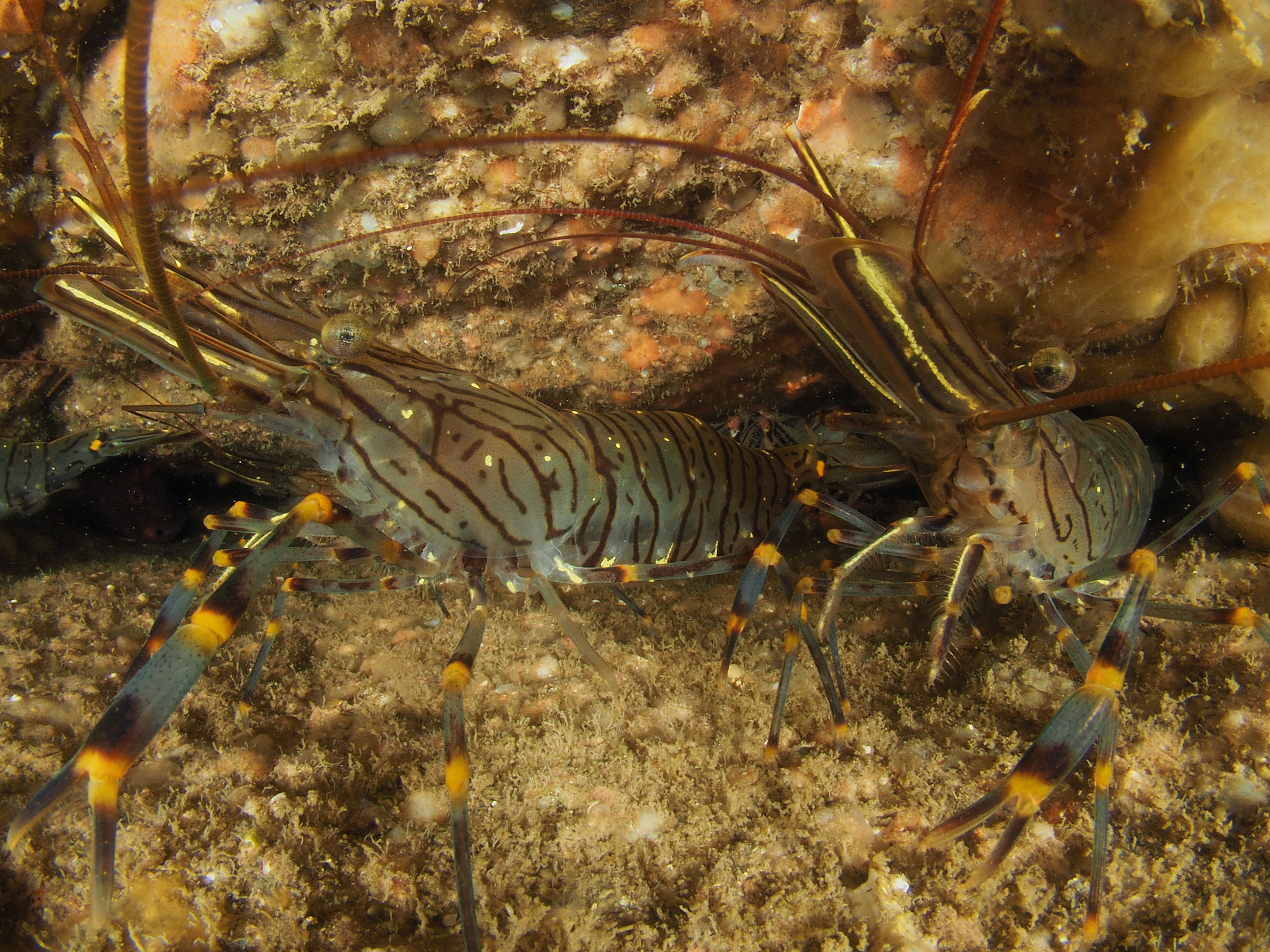
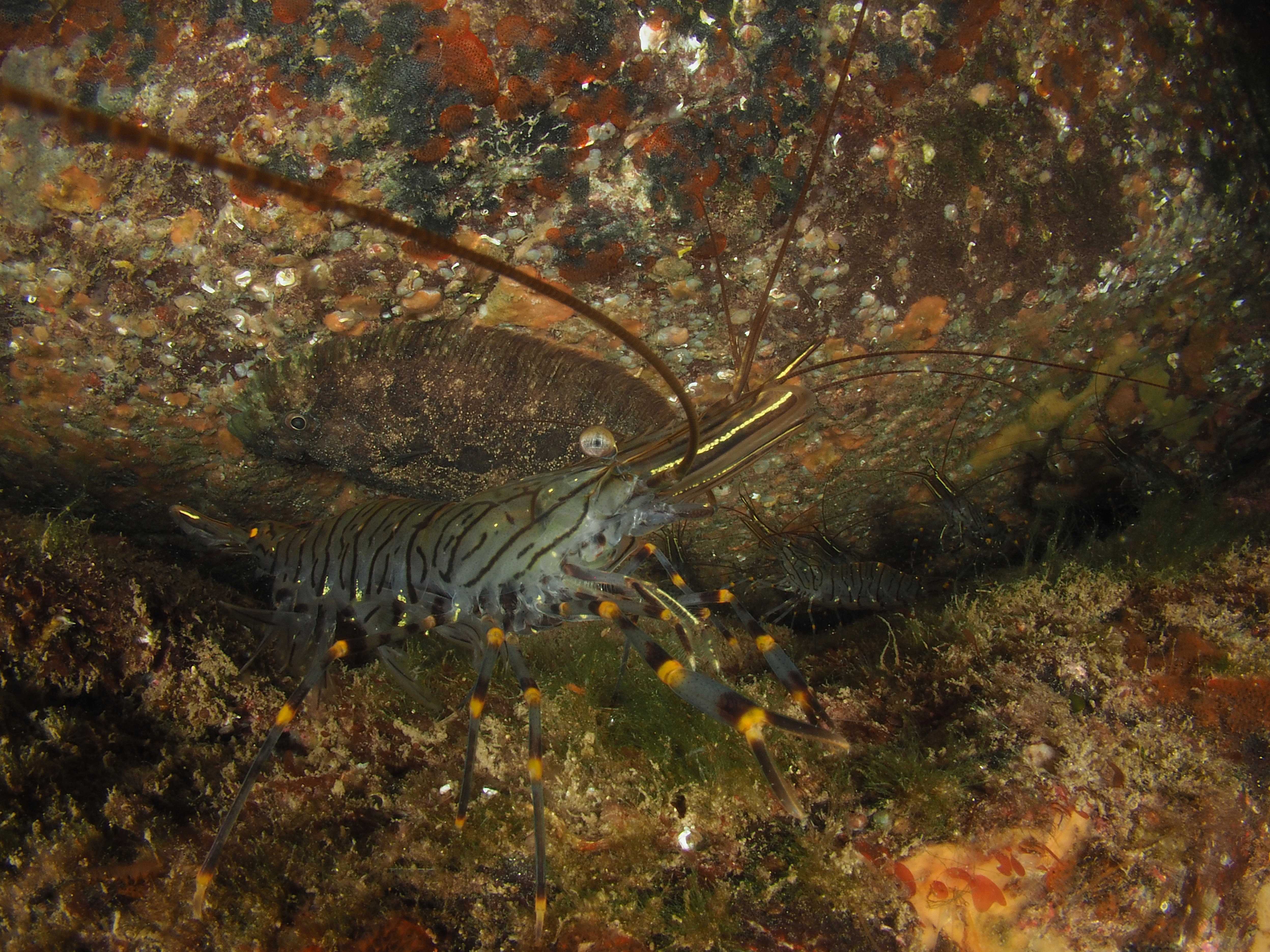
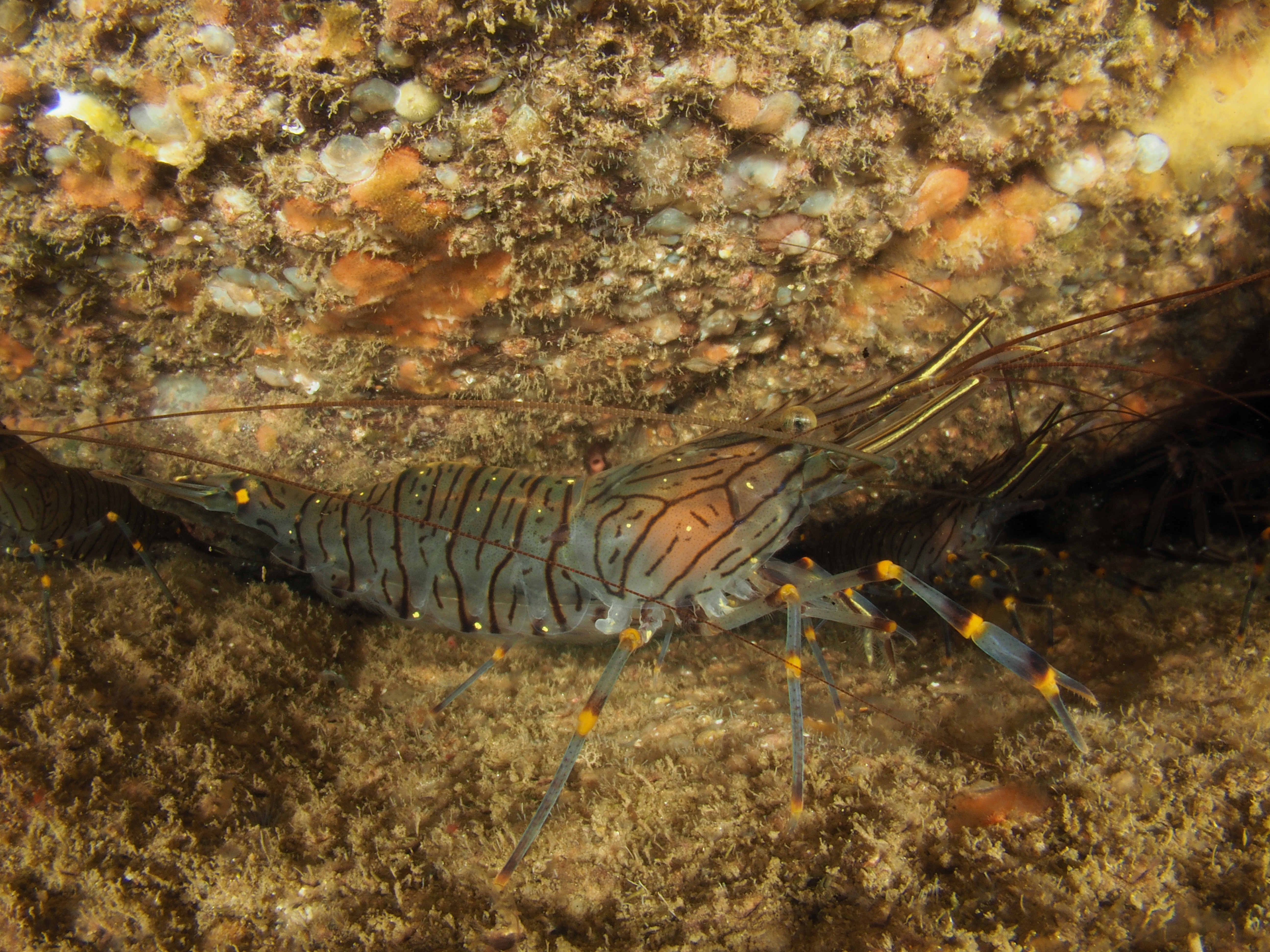
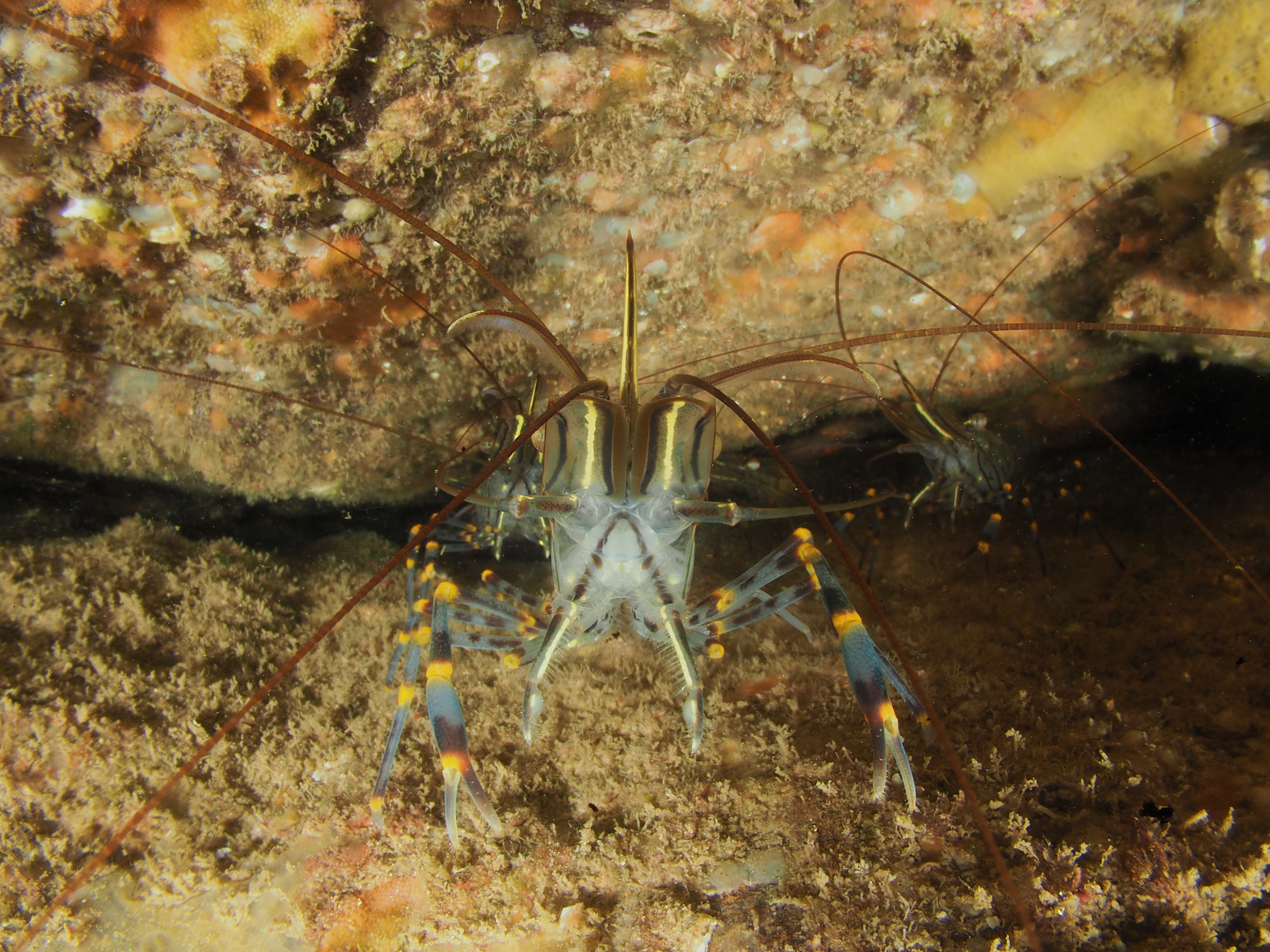
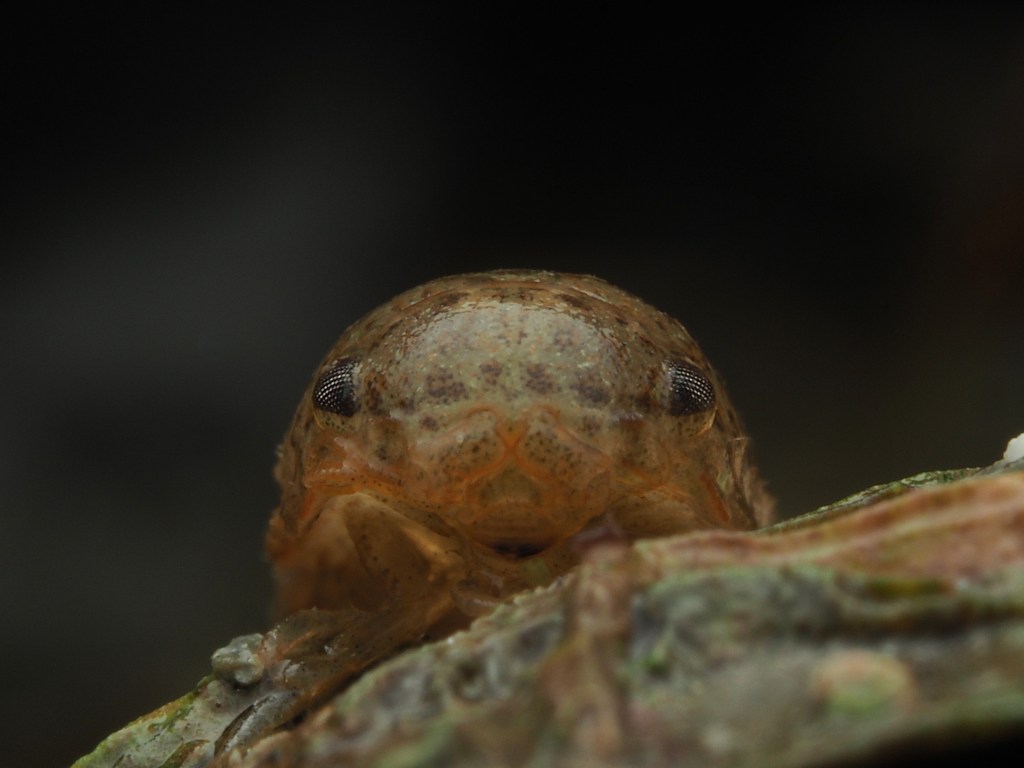
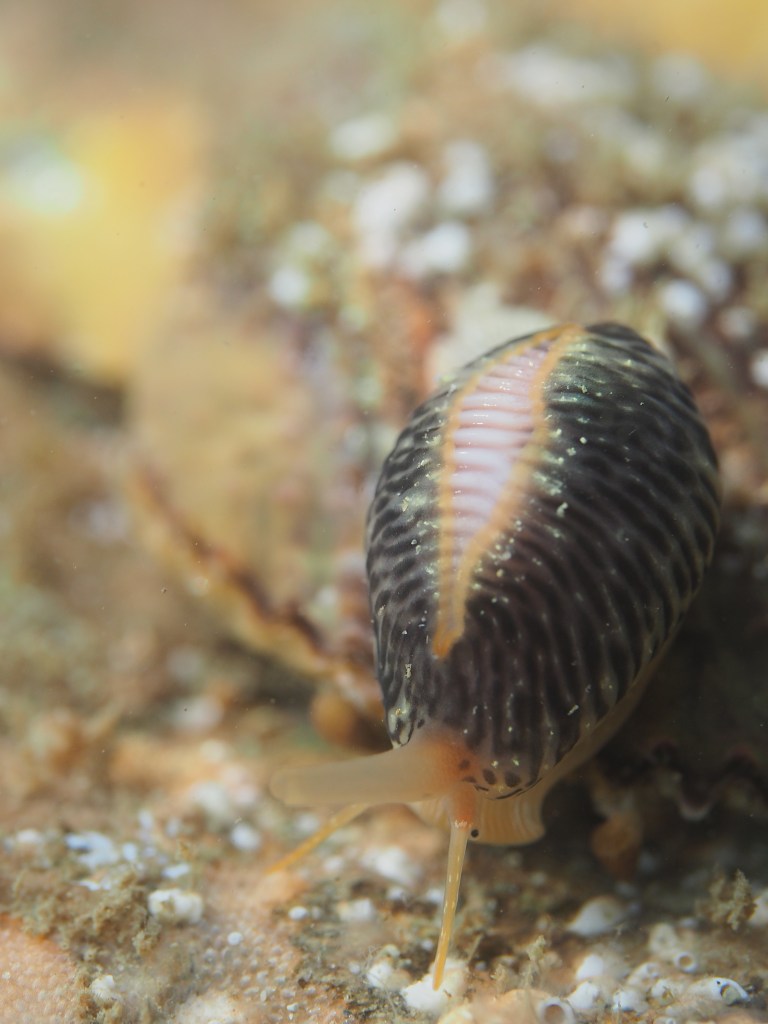
The final photo is technically not great, but I like it because it shows how a range of species apparently gets on quite well at close quarters. On the left, a Common Prawn Palaemon serratus, which can grow quite large and is actually really beautiful with its blue and yellow stripes. Right behind it is a Squat Lobster, with two Edible Crabs lurking in the background and an upside down male Connemara Clingfish Lepadogaster candolii – the next post will be about the fish of Silver Steps!




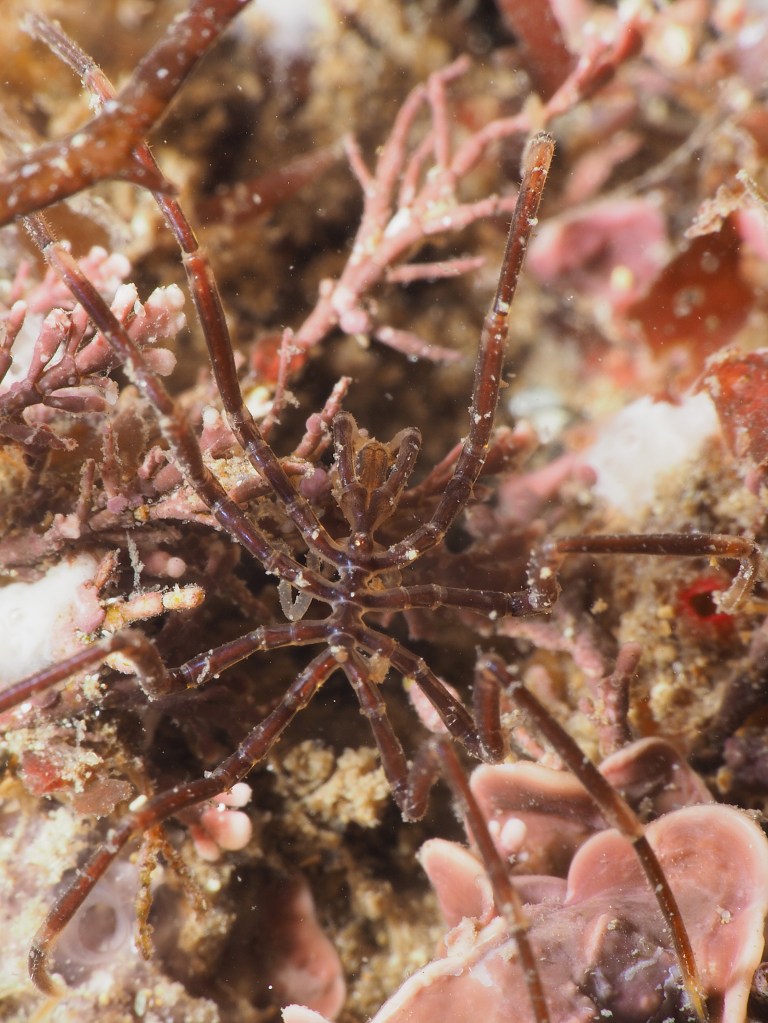
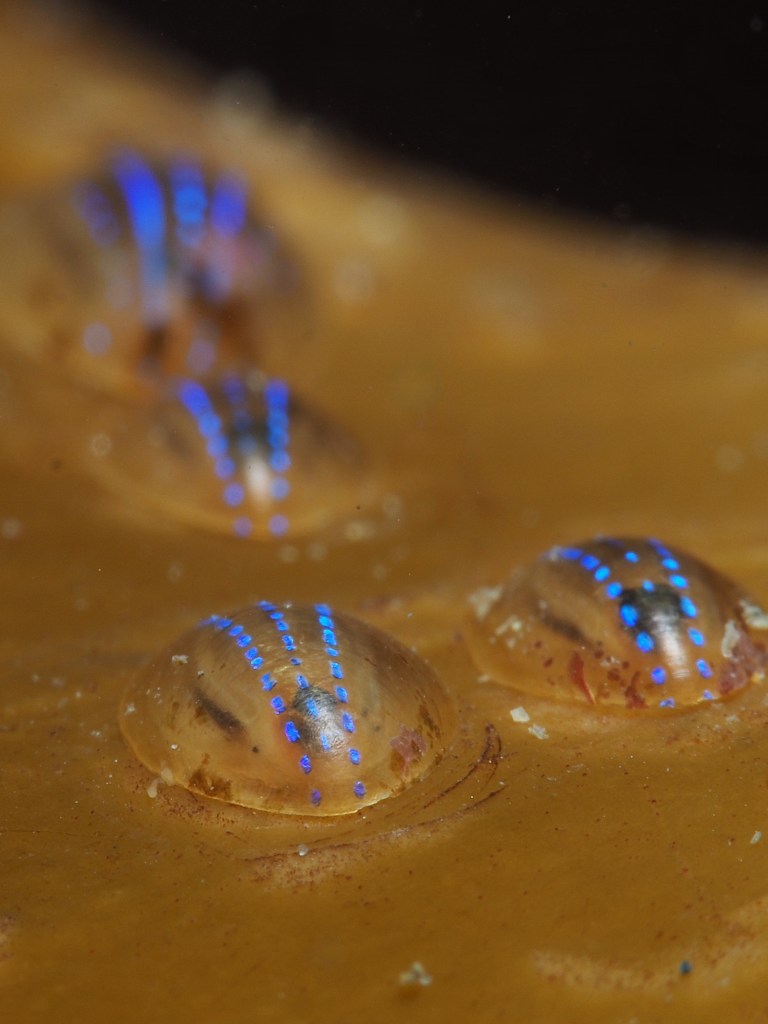
Many other critters were found too and I took shots of a selection. First, a Sea Spider, all legs and crawling away. A tiny mat of colonial tunicate that looked like a persian rug on drugs. A quick shot of the ubiquitous (if you know where to look – on kelp fronds) blue-rayed Limpets and a stalked jellyfish. Finally, I spent a lot of time taking shallow-depth-of-field AND slow shutter-speed photos of a scorpion spider crab in a snakelocks anemone to get some sort of ‘artistic’ shot. It did not really work, but it was fun nonetheless and I will have a go at it again. After almost 2,5 hours in the water I stumbled back to the car to get changed – an afternoon well-spent!
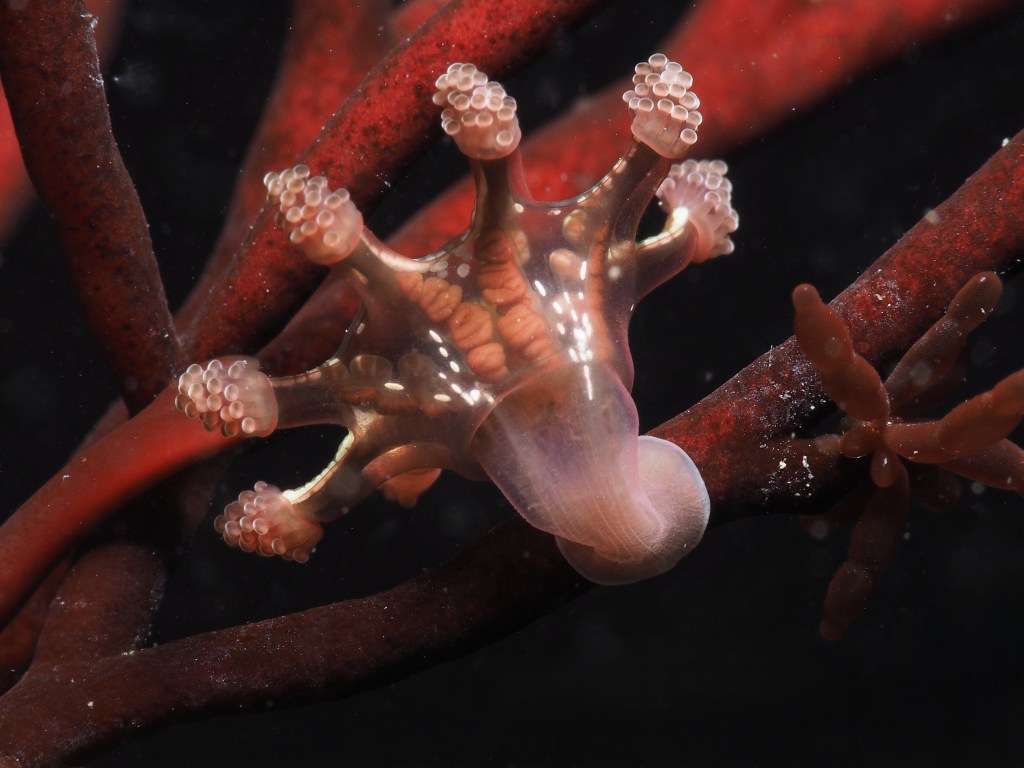
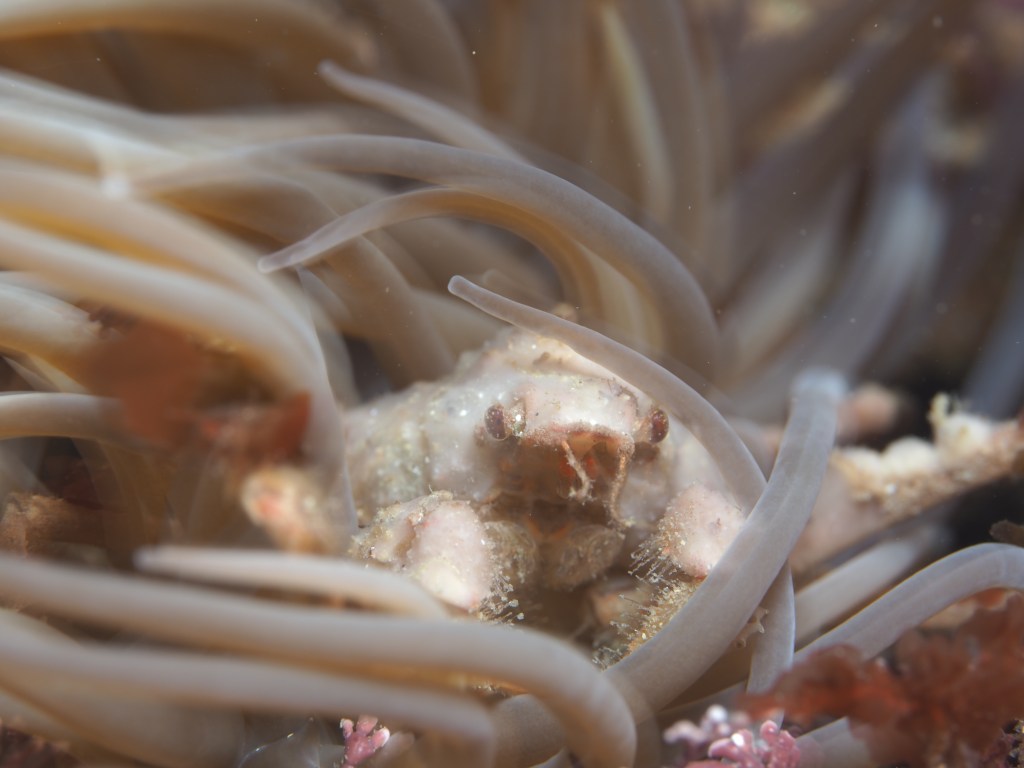
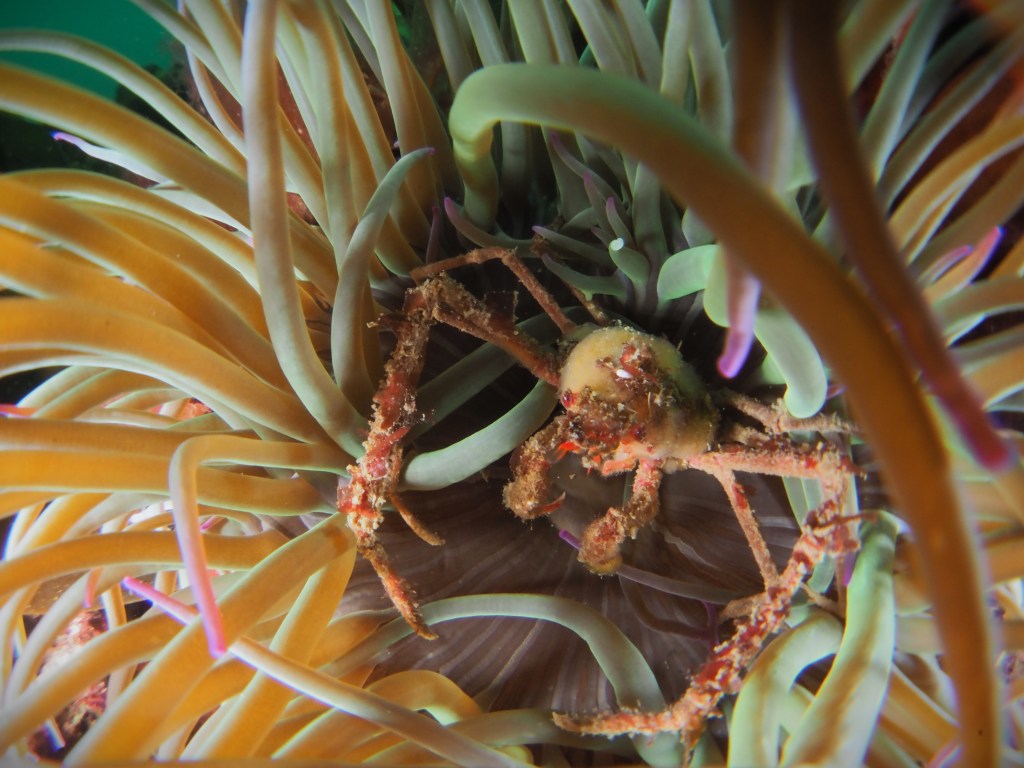






This seems like a familiar way to start a blog post but here I go again: ‘the weather has been terrible lately and I have not been in the water!’. March used to be my favourite time for snorkeling because the seaweeds look at their best, but the last three years it has been windy and wet, surely because of climate change…
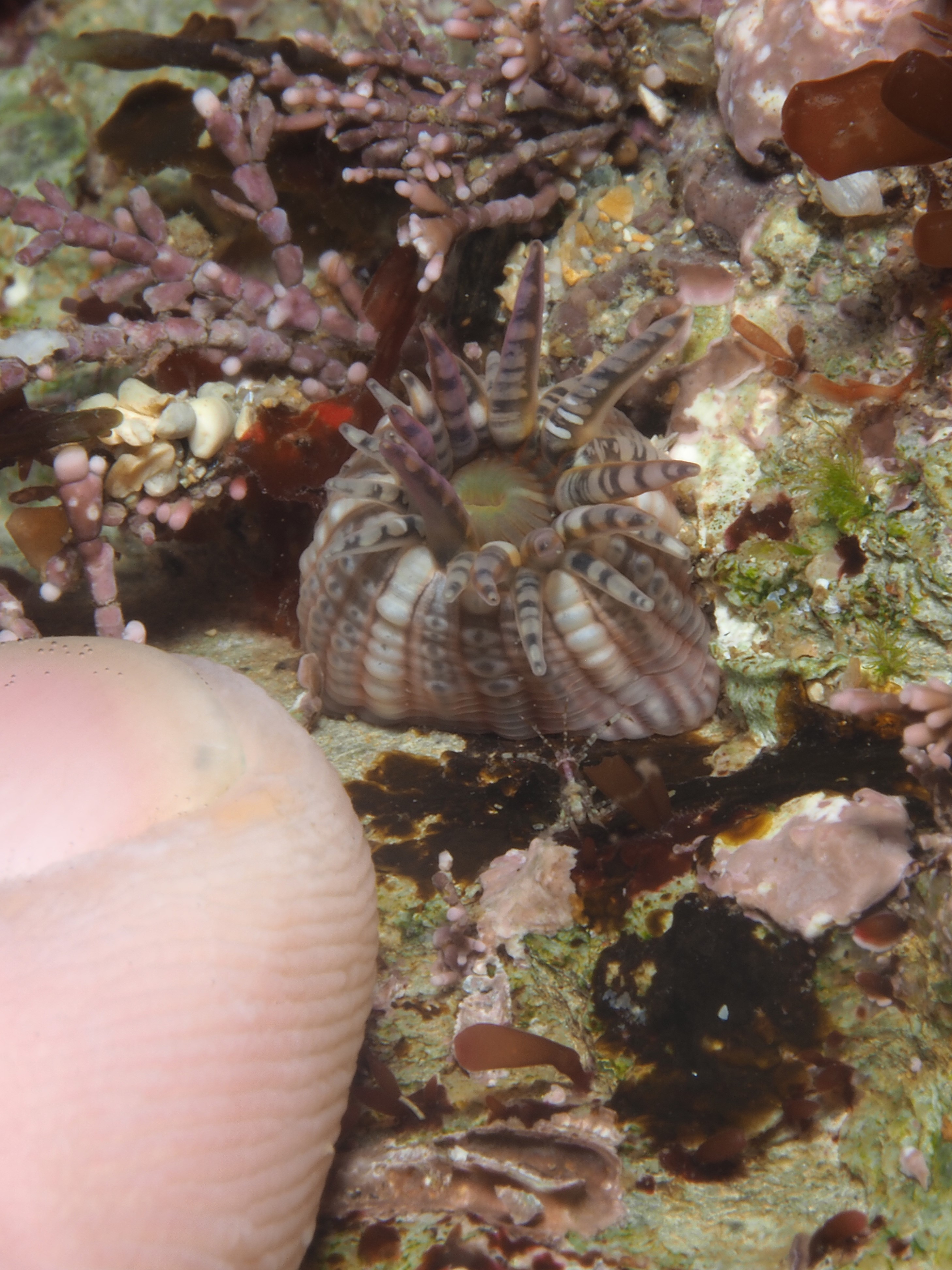
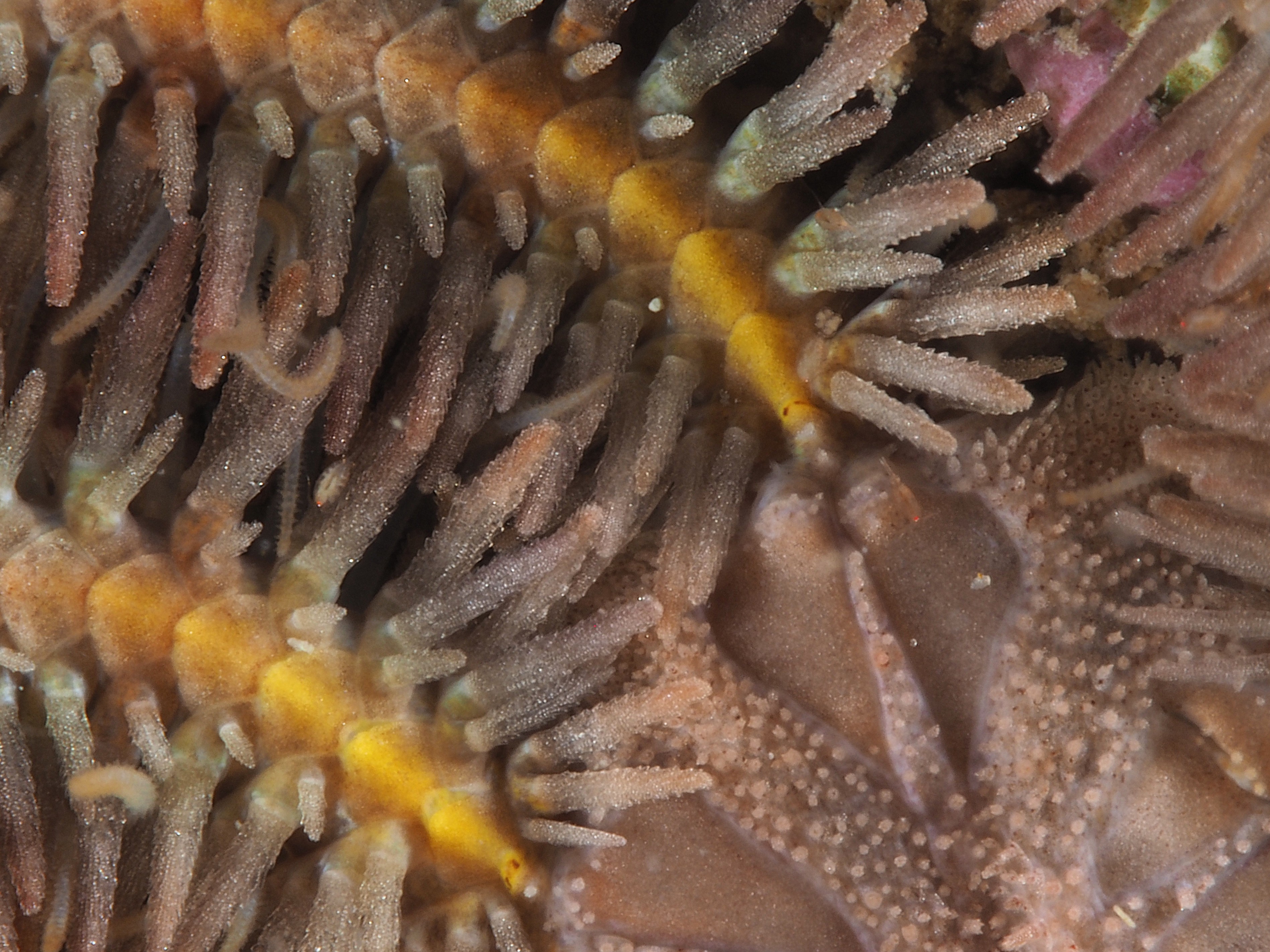
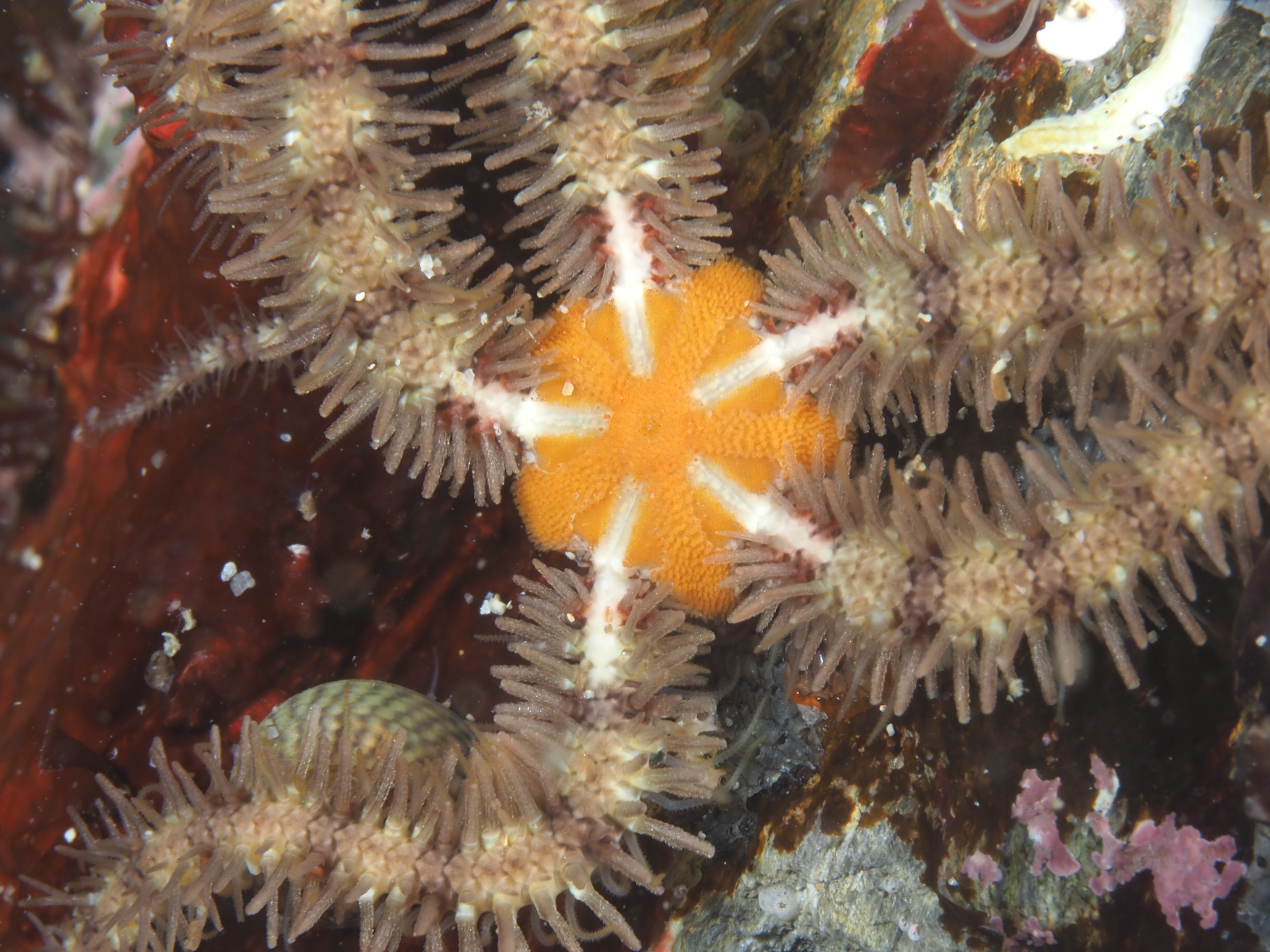
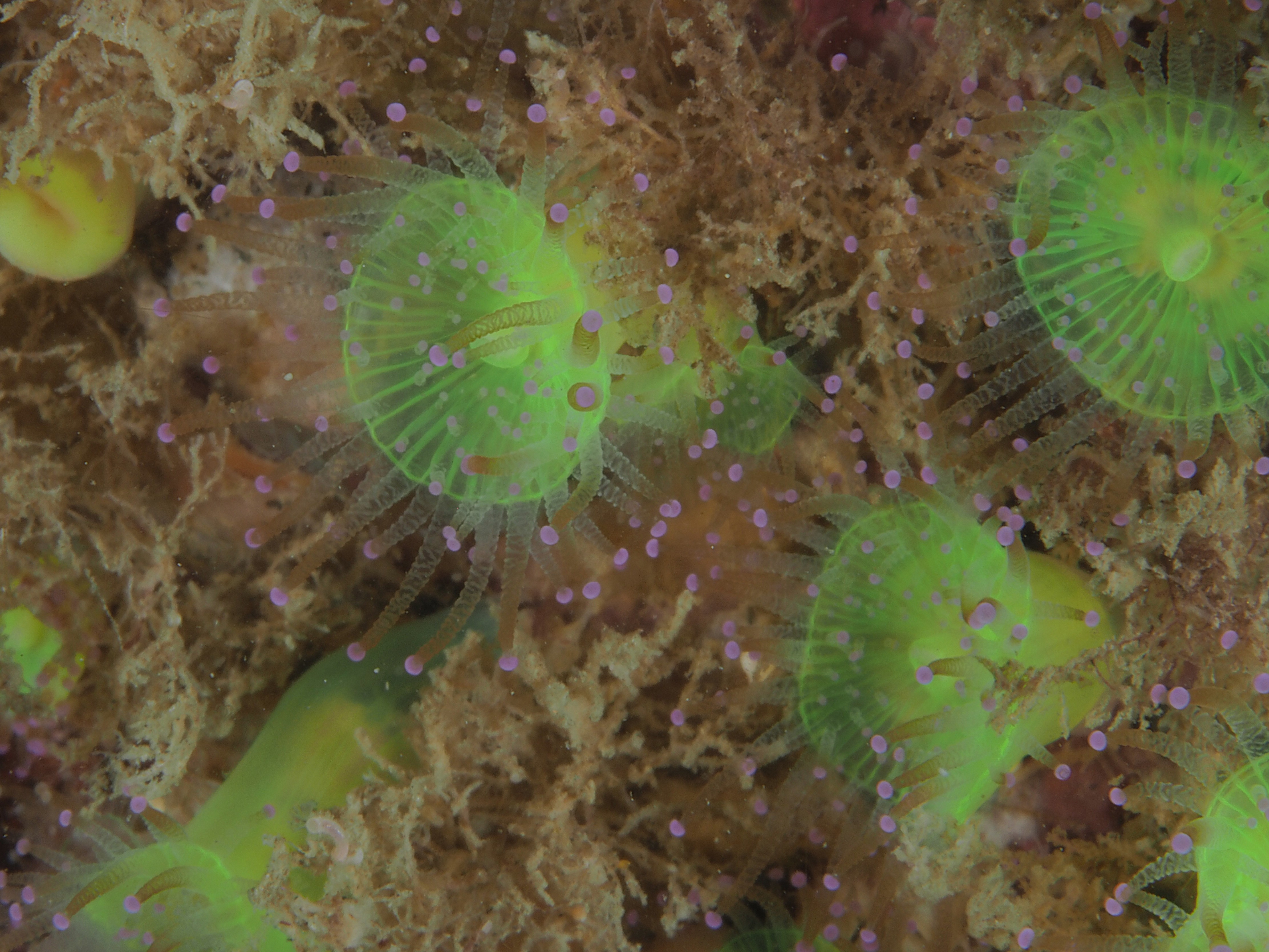
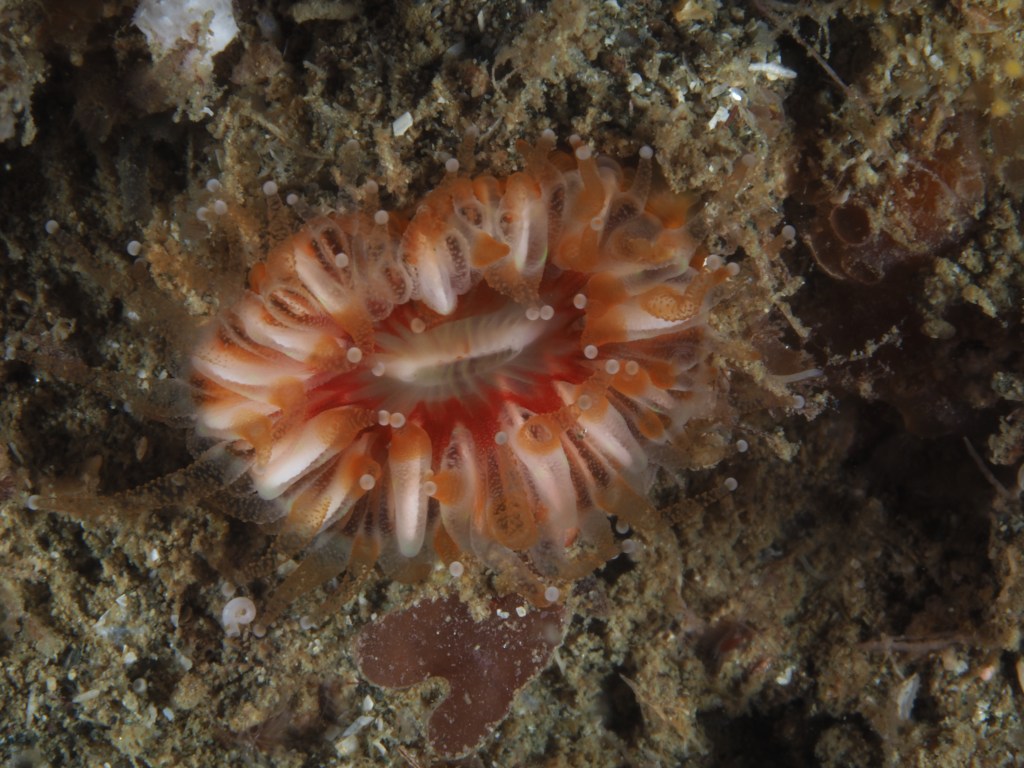
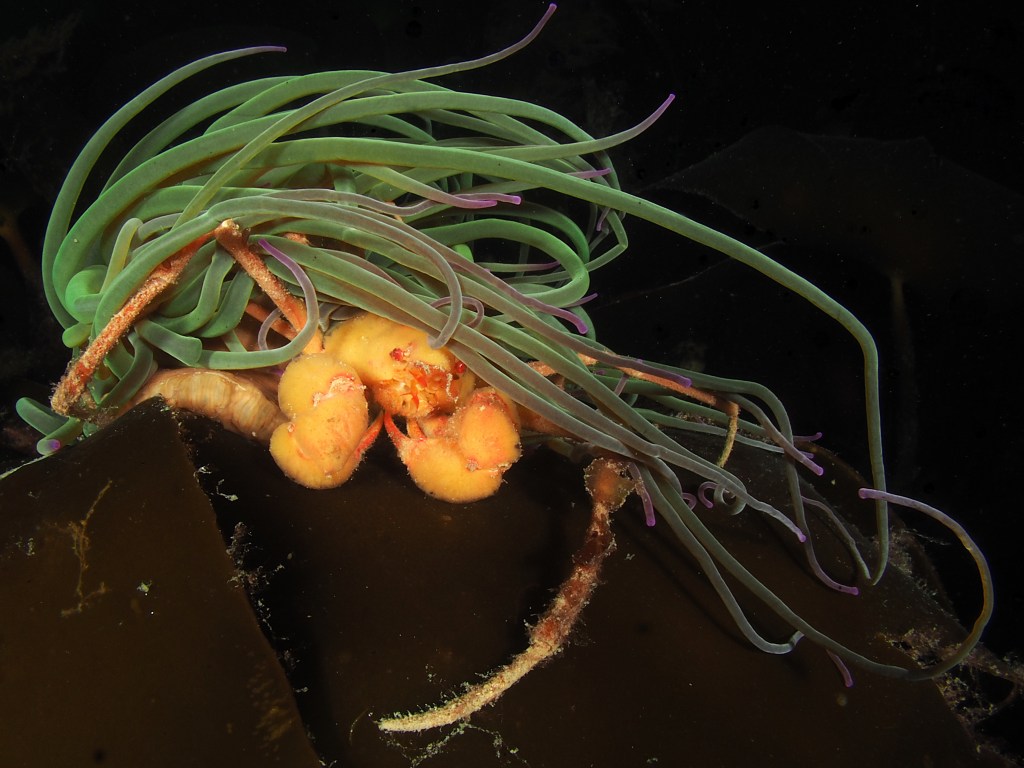
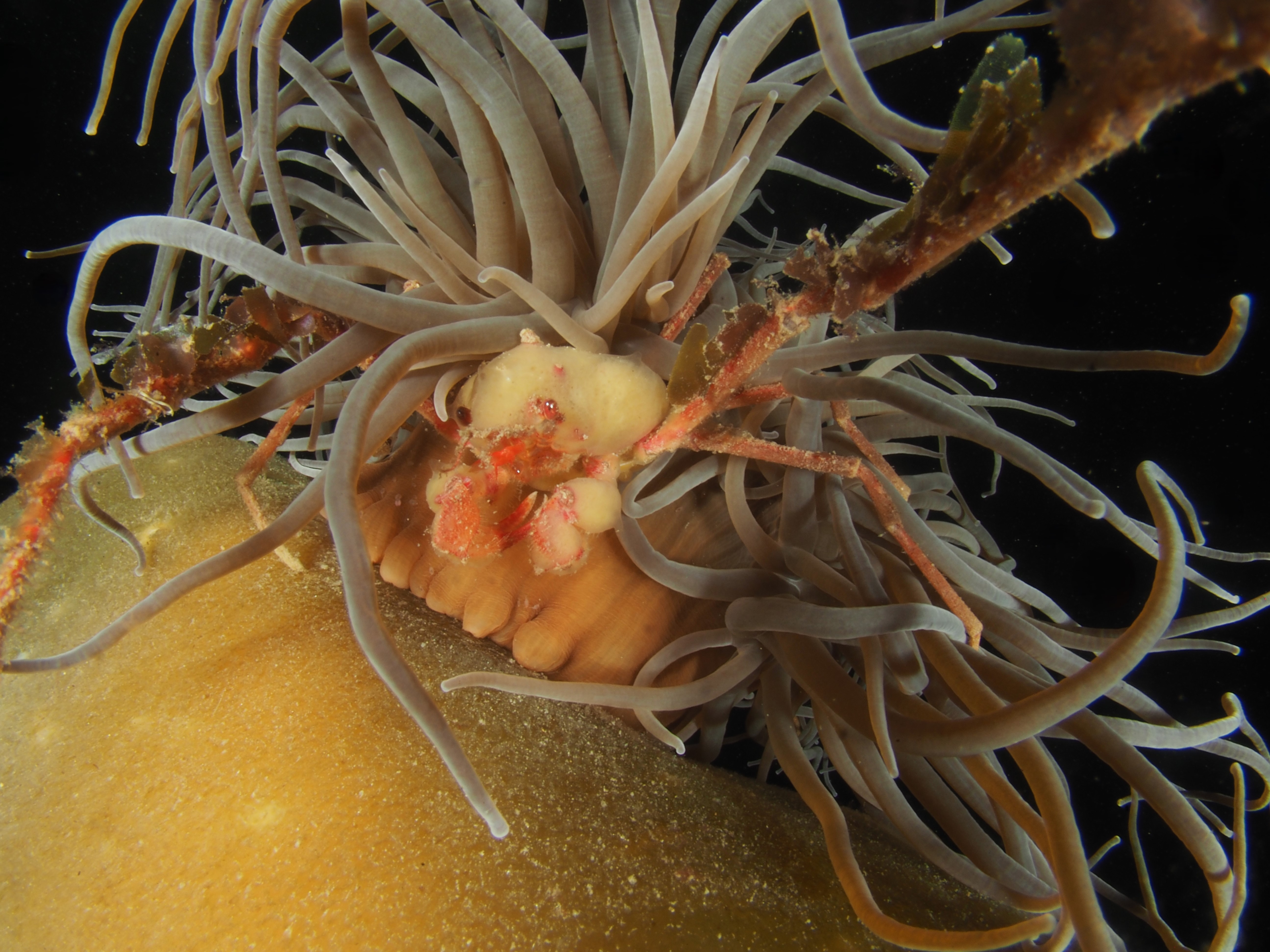
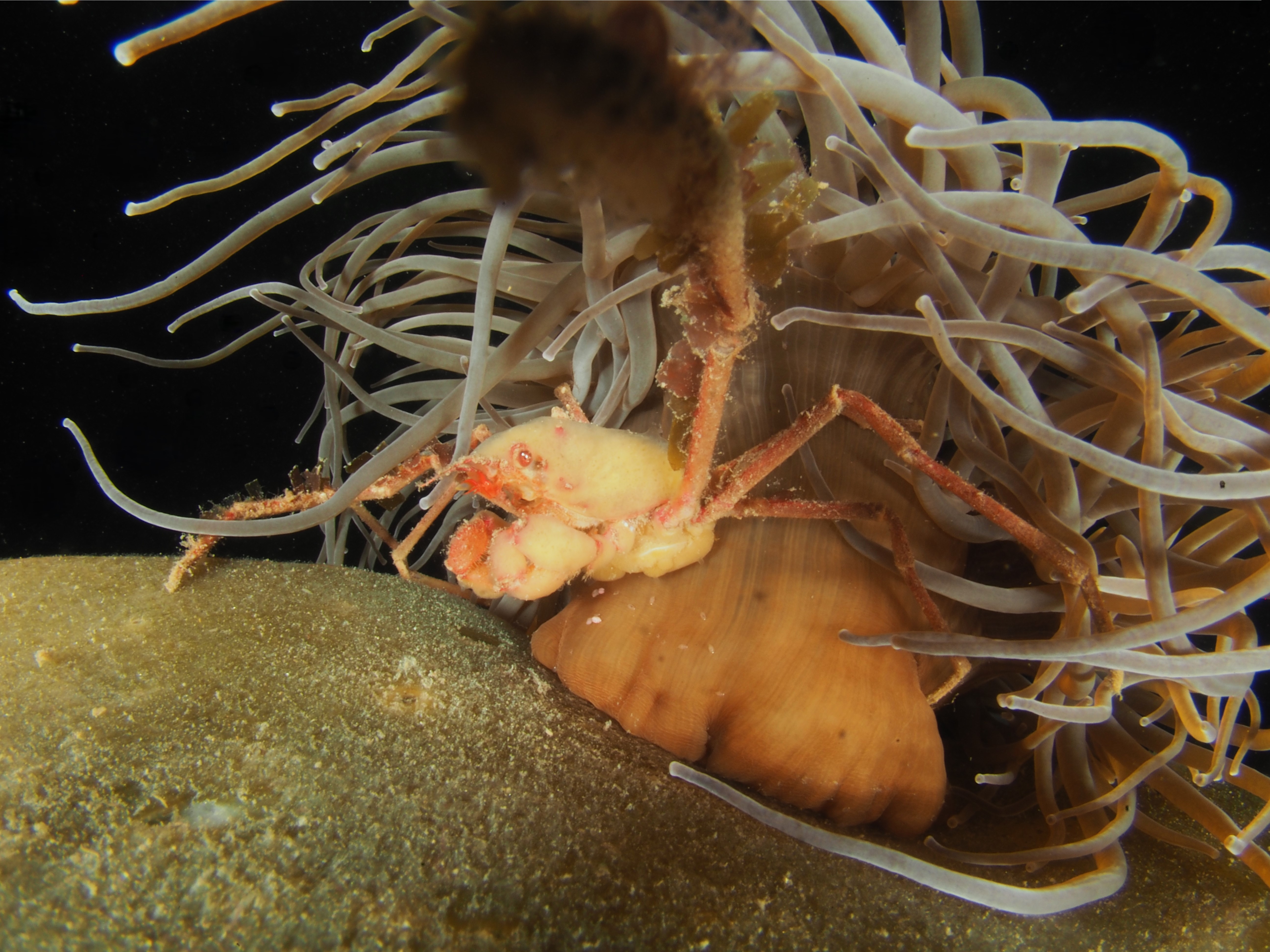
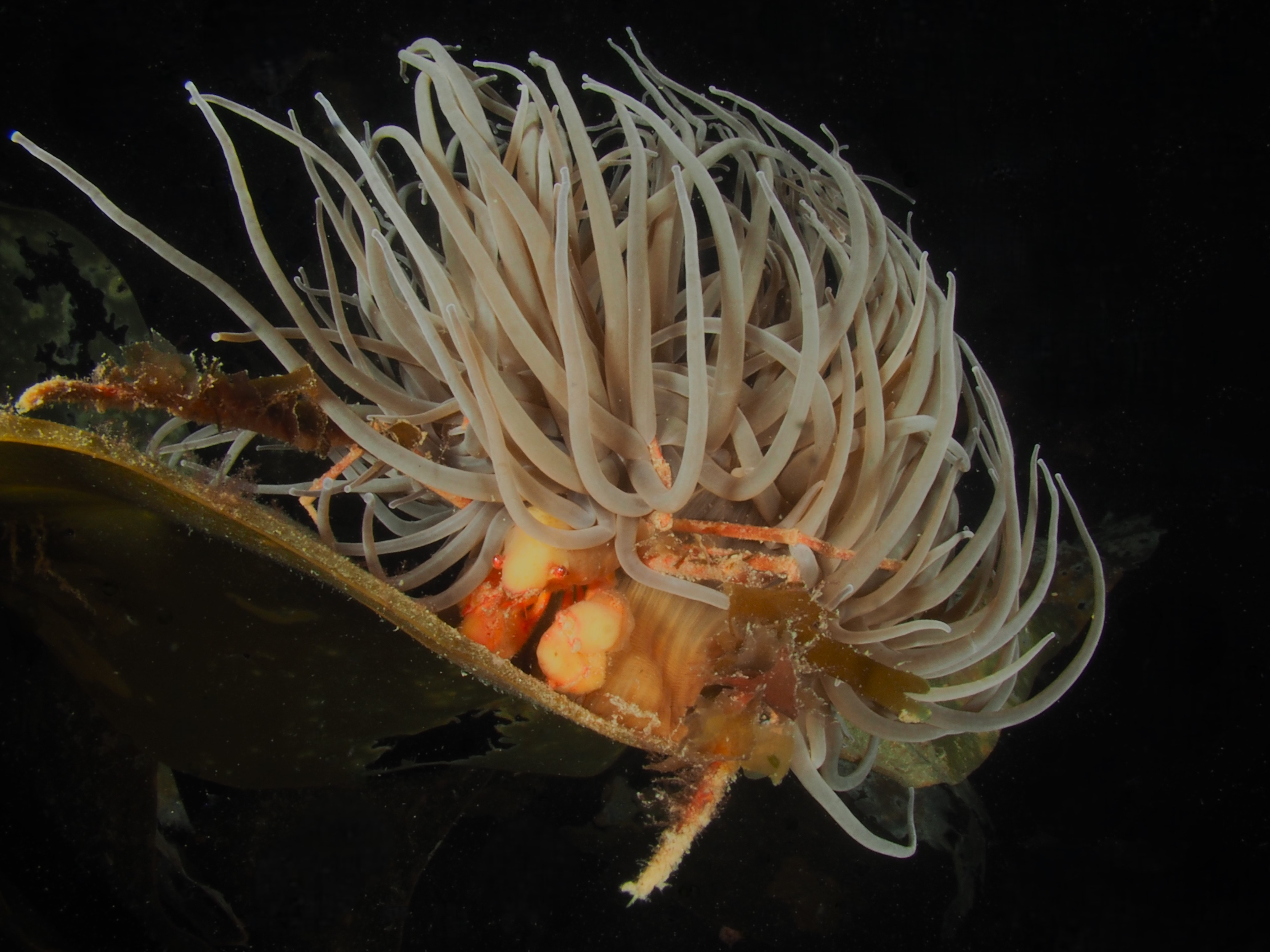
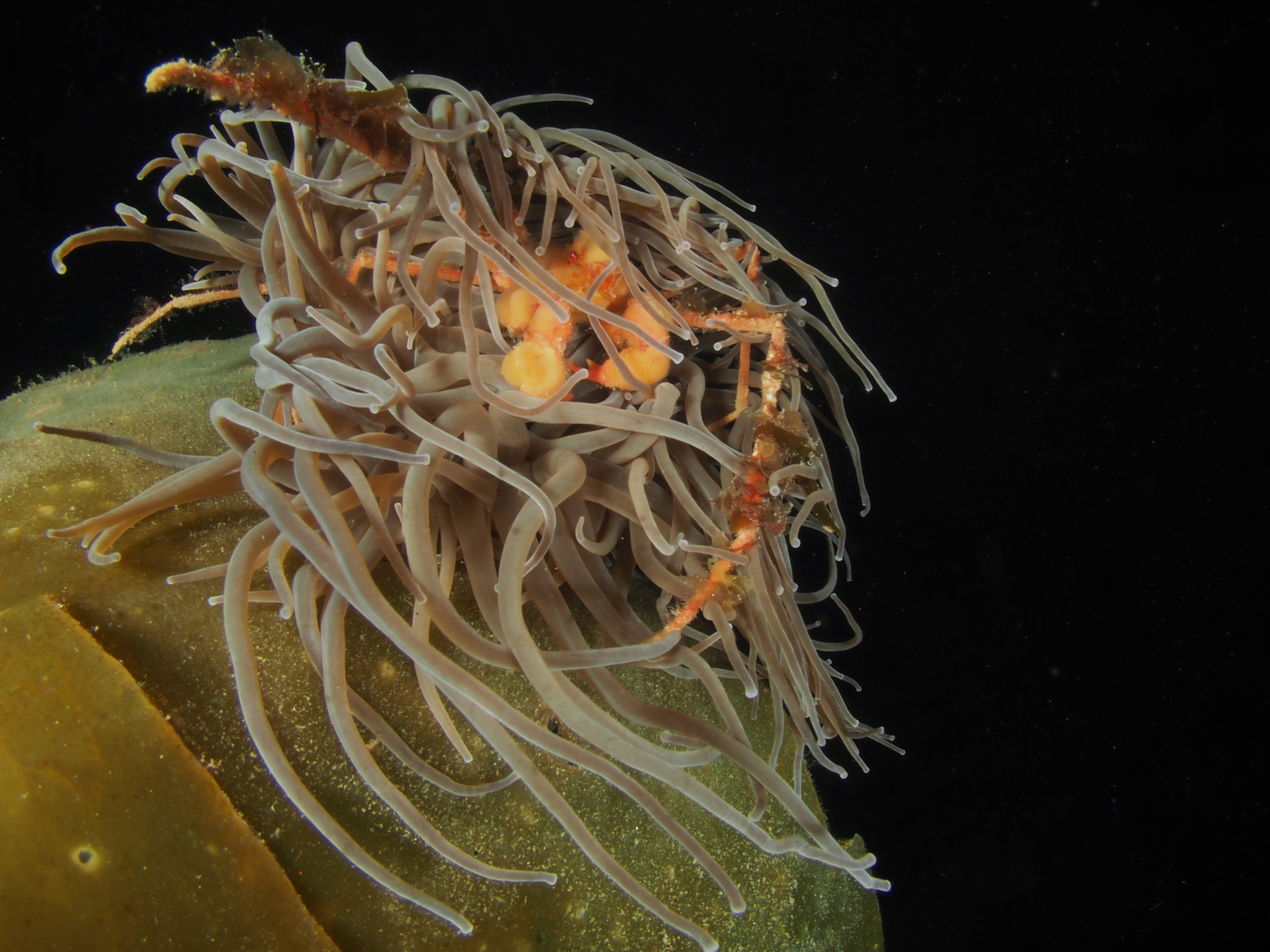
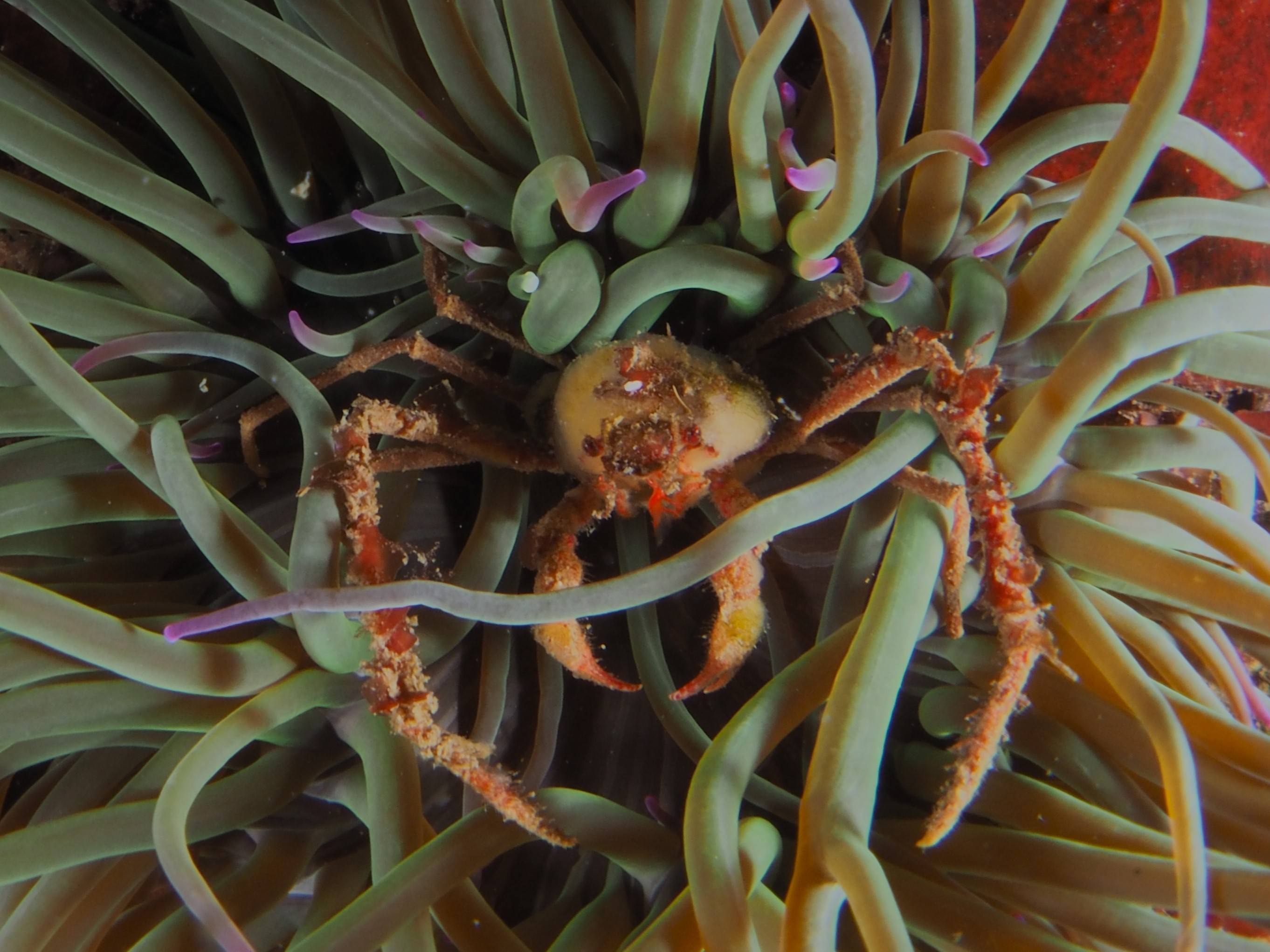
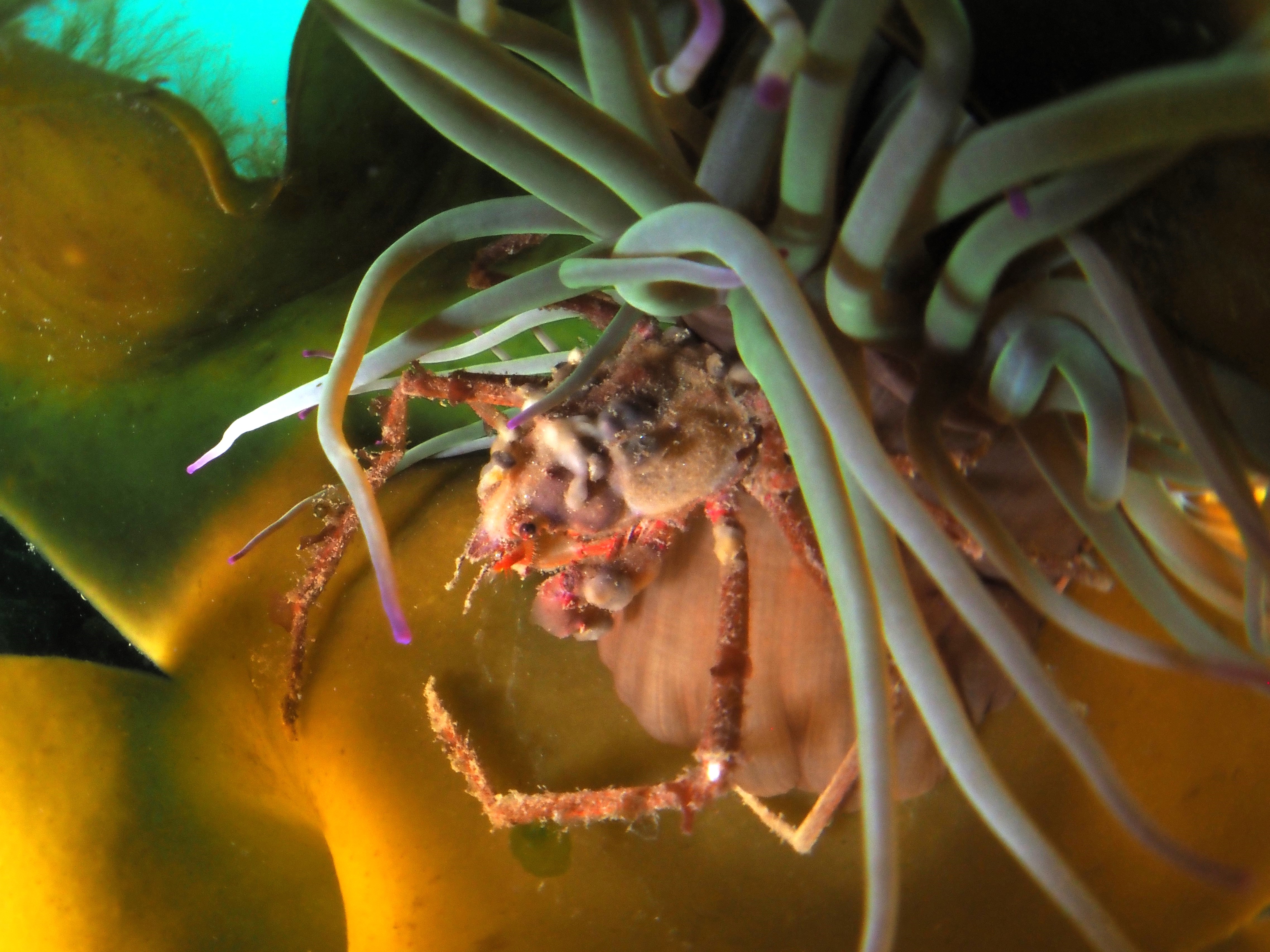
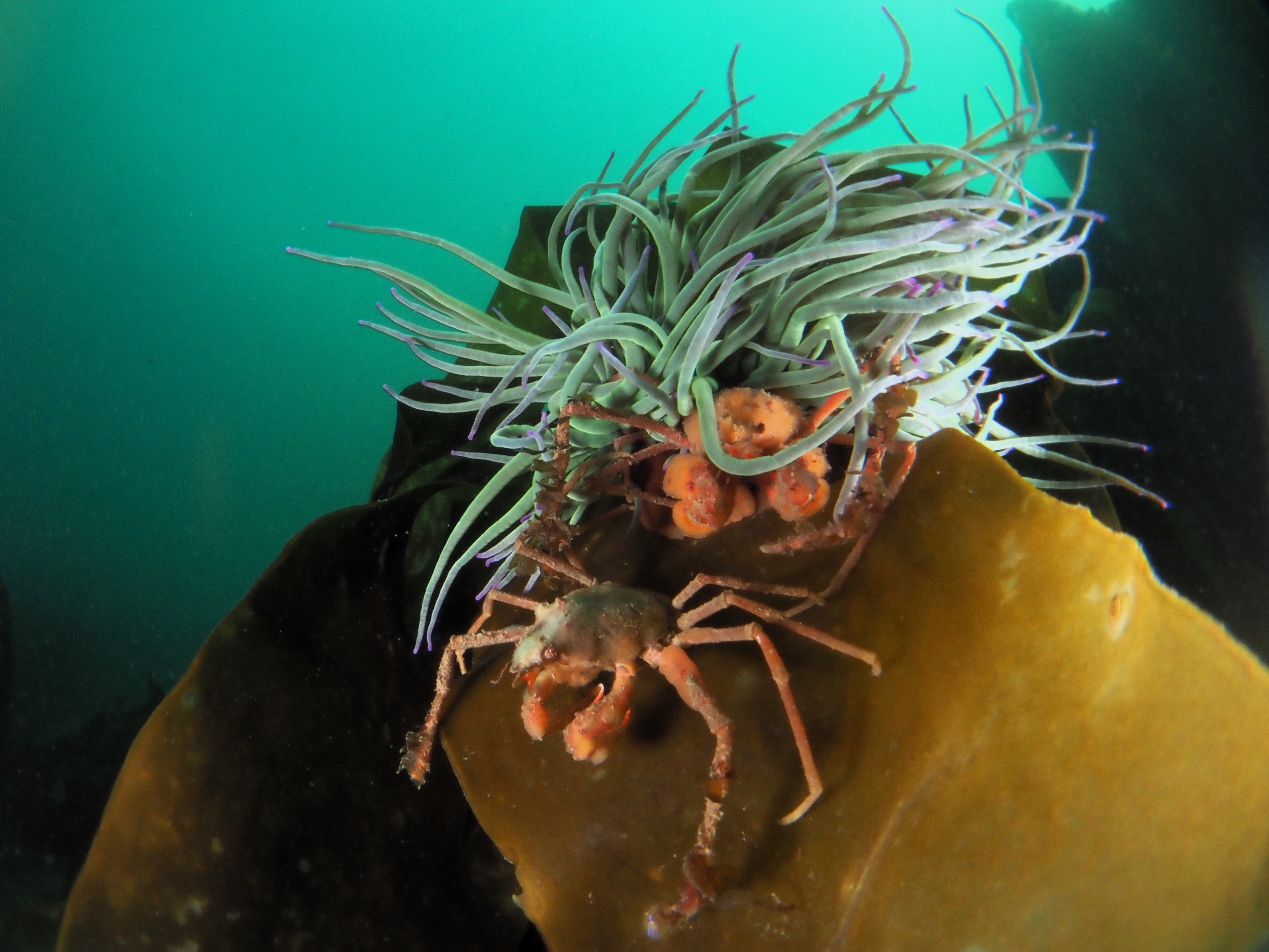
To keep the blog going (a bit), I have dug out some images from a few dives last year featuring Inachus spider crabs. There are three species, I. phalangium, I. dorsettensis and I. leptochirus, which can be told apart by the arrangement of tubercules on their carapace, but these are often obscured by epiphyte growth, and so I am keeping it to Inachus sp. All species are associated with Snakelocks Anemone (Anemonia viridis) hosts. The photo above is taken using a weird ‘wide angle macro’ wetlens (INON UFL-M150 ZM80). This perspective always fascinated me but it is difficult to achieve. This lens does the job, although it is incredibly ‘soft’, especially around the edges. The close focusing also makes it difficult to direct the strobe light on the subject. So there is a tradeoff between getting the surroundings in view and sharpness. Below first some sharper shots using my 60mm macrolens, followed by some macro wide angle shots (they happen to be each of the different Anemonia colour morph):
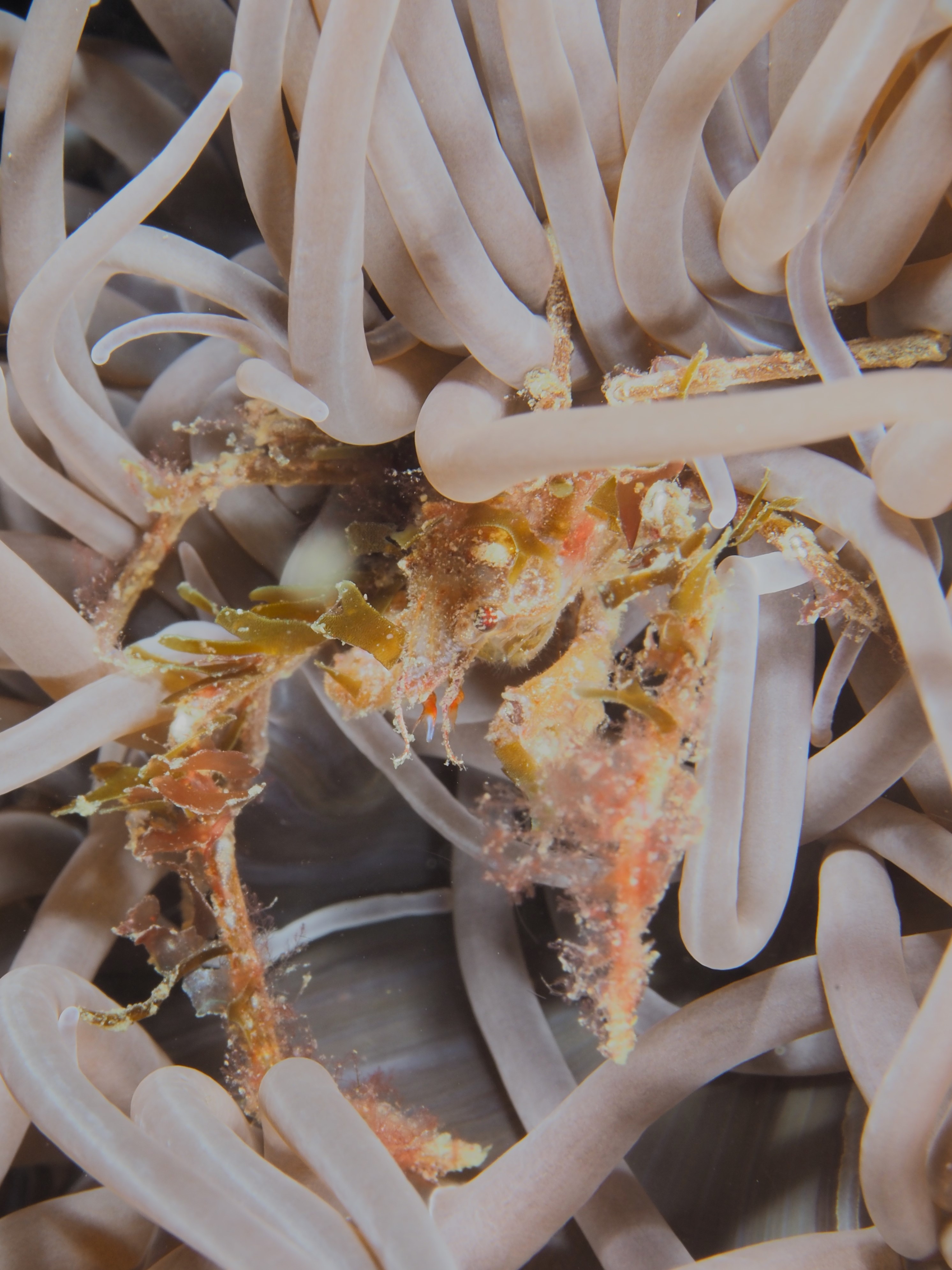







I will leave you with the following interesting bit on the biology of these crabs by Diesel (Ethology, 1986):
I. phalangium females are site-constant, and live in the protection of one anemone or group. Males travel frequently between anemones harbouring females due to spawn; they copulate and guard the females until spawning, after which the male leaves again. A male operates in a patrol area containing 3-8 anemone groups and up to 8 females, visiting each female in turn repeatedly just before it is due to spawn. Patrol areas of different males may overlap, with resulting competition to fertilize a female’s next brood. Large males have higher reproductive success than small ones. Females live up to 8 months after the moult of puberty and hatch up to six broods, and males live up to 7 months as adults. A male could fertilize a calculated 26,000 eggs, whilst a female’s reproductive potential is ca. 4,200 eggs. Mortality risks are higher for males than for females, probably because of increased predation while leaving the protection of anemones in order to visit females. Males learn the positions of anemones harbouring females in their patrol areas, and when these are due to spawn. This allows a male to travel with a target and arrive punctually to fertilize the next brood due in his circuit. I. phalangium is the first marine invertebrate reported to use a “schedule” of localities and times for visiting prespawning females. In this way males minimize searching time and mortality risk, and maximize the number of broods fertilized.